
作者: [美] 弗里曼
出版社: 中国电力出版社
译者: O'Reilly Taiwan公司
出版年: 2007-9
页数: 637
定价: 98.00元
装帧: 平装
丛书: O'Reilly深入浅出系列
ISBN: 9787508353937
- 1.策略模式-封装行为
- 2.观察者模式-封装依赖
- 3.装饰者模式-装饰对象
- 4. 工厂模式
- 5.单例模式(单件模式)
- 6.命令模式-封装调用
- 7.适配器模式与外观模式-随遇而安
- 8.模板方法模式-封装算法
- 送代器与组合模式-管理良好的集合
- 10 状态模式-事物的状态
- 11.代理模式-控制对象访问
1.策略模式-封装行为
设计原则-找出应用中可能需要变化之处,把它们独立出来,不要和那些不需要变化的代码混在一起。换句话说,如果每次新的需求一来,都会使某方面的代码发生变化,那么你就可以确定,这部分代码需要被抽出来,和其他稳定的代码有所区分。这个原则的另一种思考方式:“把会变化的部分取出并封装起来,以便以后可以轻易地改动或扩充此部分,而不影响不需要变化的其他部分”。
设计原则-针对接口编程,而不是针对实现编程。“针对接口编程”,关键就在多态。利用多态,程序可以针对超类型编程,执行时会根据实际状况执行真正的行为,不会被绑死在超类型的行为上。“针对超类型编程”这句话,可以更明确地说成“变量的声明类型应该是超类型,通常是一个抽象类或者是一个接口,如此,只要是具体实现此超类型的类所产生的对象,都可以指定给这个变量。这也意味着,声明类时不用理会以后执行时的真正对象类型”。
策略模式-定义了算法簇,分别封装起来,让它们之间可以互相替换,此模式让算法的变化独立于使用算法的客户。
在“鸭子”这个例子中,变化的是fly()和quack()。这里把这两种行为抽出来,委托(delegate)给别人来处理。

示例代码:
Duck.java
package net.dp.strategy;
import net.dp.strategy.fly.FlyBehavior;
import net.dp.strategy.quack.QuackBehavior;
public abstract class Duck {
protected FlyBehavior flyBehavior;
protected QuackBehavior quackBehavior;
public abstract void display();
public void performFly(){
flyBehavior.fly();
}
public void performQuack(){
quackBehavior.quack();
}
public void swim(){
System.out.println("All ducks float, even decoys!");
}
public void setFlyBehavior(FlyBehavior flyBehavior) {
this.flyBehavior = flyBehavior;
}
public void setQuackBehavior(QuackBehavior quackBehavior) {
this.quackBehavior = quackBehavior;
}
}
FlyBehavior.java
package net.dp.strategy.fly;
public interface FlyBehavior {
void fly();
}
QuackBehavior.java
package net.dp.strategy.quack;
public interface QuackBehavior {
void quack();
}
FlyNoWay.java
package net.dp.strategy.fly;
public class FlyNoWay implements FlyBehavior{
public void fly(){
System.out.println("I can't fly.");
}
}
FlyWithWings.java
package net.dp.strategy.fly;
public class FlyWithWings implements FlyBehavior {
public void fly() {
System.out.println("I'm flying!");
}
}
Quack.java
package net.dp.strategy.quack;
public class Quack implements QuackBehavior{
public void quack(){
System.out.println("quack");
}
}
MuteQuack.java
package net.dp.strategy.quack;
public class MuteQuack implements QuackBehavior{
public void quack(){
System.out.println("<<Silence>>");
}
}
Squeak.java
package net.dp.strategy.quack;
public class Squeak implements QuackBehavior{
public void quack(){
System.out.println("Squeak");
}
}
ADuck.java
package net.dp.strategy;
import net.dp.strategy.fly.FlyNoWay;
import net.dp.strategy.fly.FlyWithWings;
import net.dp.strategy.quack.MuteQuack;
import net.dp.strategy.quack.Squeak;
public class ADuck extends Duck {
public ADuck() {
flyBehavior = new FlyWithWings();
quackBehavior = new Squeak();
}
public void display() {
System.out.println("I'm a duck model.");
}
public void changeBehavior() {
setFlyBehavior(new FlyNoWay());
setQuackBehavior(new MuteQuack());
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ADuck aDuck = new ADuck();
aDuck.display();
aDuck.swim();
aDuck.performFly();
aDuck.performQuack();
aDuck.changeBehavior();
aDuck.performFly();
aDuck.performQuack();
}
}
方法changeBehavior()显示了运行时改变策略的威力。
设计原则-多用组合,少用继承。使用组合建立系统具有很大的弹性,不仅可将算法封装成类,更可以“在运行时动态地改变行为”,只要组合的行为对象符合正确的接口标准即可。
2.观察者模式-封装依赖
观察者模式-定义了对象之间的一对多依赖,这样一来,当一个对象改变状态时,它的所有依赖者都会收到通知并自动更新。
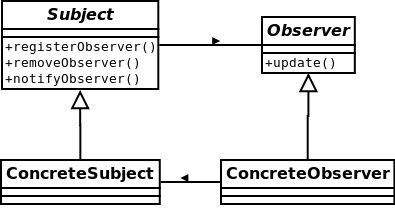
设计原则-为了交互对象之间的松耦合设计而努力。对于观察者模式而言,改变主题或观察者其中一方,并不会影响另一方。因为两者是松耦合的,所以只要他们之间的接口仍被遵守,我们就可以自由地改变他们。
天气预报主题(WeatherData)需要监控temperature,humidity和pressure三个数据,如果发生变化,需要通知相应的观察者。
示例代码: Subject.java
package net.dp.observer;
public interface Subject {
void registerObserver(Observer o);
void removeObserver(Observer o);
void notifyObservers();
}
Observer.java
package net.dp.observer;
public interface Observer {
void update(float temp,float humidity, float pressure);
}
DisplayElement.java
package net.dp.observer;
public interface DisplayElement {
void display();
}
WeatherData.java
package net.dp.observer;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class WeatherData implements Subject {
private ArrayList<Observer> observers;
private float temperature;
private float humidity;
private float pressure;
public WeatherData() {
observers = new ArrayList<Observer>();
}
public void registerObserver(Observer o) {
observers.add(o);
}
public void removeObserver(Observer o) {
int i = observers.indexOf(o);
if (i >= 0) {
observers.remove(i);
}
}
public void notifyObservers() {
for (int i = 0; i < observers.size(); i++) {
Observer observer = (Observer) observers.get(i);
observer.update(temperature, humidity, pressure);
}
}
public void measurementsChanged() {
notifyObservers();
}
public void setMeasurements(float temperature, float humidity,
float pressure) {
this.temperature = temperature;
this.humidity = humidity;
this.pressure = pressure;
measurementsChanged();
}
// other WeatherData methods here
public float getTemperature() {
return temperature;
}
public float getHumidity() {
return humidity;
}
public float getPressure() {
return pressure;
}
}
CurrentConditionsDisplay.java
package net.dp.observer;
public class CurrentConditionsDisplay implements Observer, DisplayElement {
private float temperature;
private float humidity;
public CurrentConditionsDisplay(Subject weatherData) {
weatherData.registerObserver(this);
}
public void update(float temperature, float humidity, float pressure) {
this.temperature = temperature;
this.humidity = humidity;
display();
}
public void display() {
System.out.println("Current conditions: " + temperature
+ "F degrees and " + humidity + "% humidity");
}
}
ForecastDisplay.java
package net.dp.observer;
public class ForecastDisplay implements Observer, DisplayElement {
private float currentPressure = 29.92f;
private float lastPressure;
public ForecastDisplay(WeatherData weatherData) {
weatherData.registerObserver(this);
}
public void update(float temp, float humidity, float pressure) {
lastPressure = currentPressure;
currentPressure = pressure;
display();
}
public void display() {
System.out.print("Forecast: ");
if (currentPressure > lastPressure) {
System.out.println("Improving weather on the way!");
} else if (currentPressure == lastPressure) {
System.out.println("More of the same");
} else if (currentPressure < lastPressure) {
System.out.println("Watch out for cooler, rainy weather");
}
}
}
StatisticsDisplay.java
package net.dp.observer;
public class StatisticsDisplay implements Observer, DisplayElement {
private float maxTemp = 0.0f;
private float minTemp = 200;
private float tempSum = 0.0f;
private int numReadings;
public StatisticsDisplay(WeatherData weatherData) {
weatherData.registerObserver(this);
}
public void update(float temp, float humidity, float pressure) {
tempSum += temp;
numReadings++;
if (temp > maxTemp) {
maxTemp = temp;
}
if (temp < minTemp) {
minTemp = temp;
}
display();
}
public void display() {
System.out.println("Avg/Max/Min temperature = "
+ (tempSum / numReadings) + "/" + maxTemp + "/" + minTemp);
}
}
HeatIndexDisplay.java
package net.dp.observer;
public class HeatIndexDisplay implements Observer, DisplayElement {
float heatIndex = 0.0f;
public HeatIndexDisplay(WeatherData weatherData) {
weatherData.registerObserver(this);
}
public void update(float t, float rh, float pressure) {
heatIndex = computeHeatIndex(t, rh);
display();
}
private float computeHeatIndex(float t, float rh) {
float index = (float) ((16.923 + (0.185212 * t) + (5.37941 * rh)
- (0.100254 * t * rh) + (0.00941695 * (t * t))
+ (0.00728898 * (rh * rh)) + (0.000345372 * (t * t * rh))
- (0.000814971 * (t * rh * rh))
+ (0.0000102102 * (t * t * rh * rh))
- (0.000038646 * (t * t * t)) + (0.0000291583 * (rh * rh * rh))
+ (0.00000142721 * (t * t * t * rh))
+ (0.000000197483 * (t * rh * rh * rh))
- (0.0000000218429 * (t * t * t * rh * rh)) + 0.000000000843296 * (t
* t * rh * rh * rh)) - (0.0000000000481975 * (t * t * t * rh
* rh * rh)));
return index;
}
public void display() {
System.out.println("Heat index is " + heatIndex);
}
}
WeatherStation.java
package net.dp.observer;
public class WeatherStation {
public static void main(String[] args) {
WeatherData weatherData = new WeatherData();
new CurrentConditionsDisplay(weatherData);
new StatisticsDisplay(weatherData);
new ForecastDisplay(weatherData);
new HeatIndexDisplay(weatherData);
weatherData.setMeasurements(80, 65, 30.4f);
System.out.println("======================");
weatherData.setMeasurements(82, 70, 29.2f);
System.out.println("======================");
weatherData.setMeasurements(78, 90, 29.2f);
}
}
3.装饰者模式-装饰对象
设计原则-类应该对扩展开放,对修改关闭(开闭原则)。目标是允许类容易扩展,在不修改现有代码的情况下,就可搭配新的行为。
装饰者模式-动态地将责任附加到对象上。若要扩展功能,装饰者提供了比继承更有弹性的替代方案。
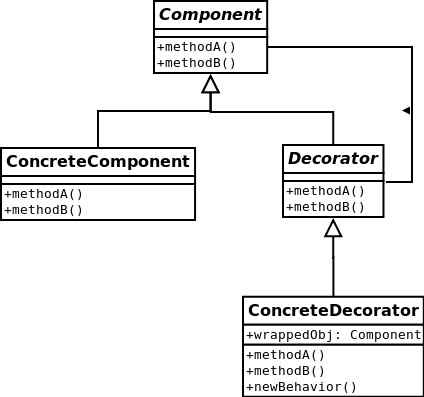
下面的例子中,Beverage是Component基类。CondimentDecorator是Decorator基类。DarkRoast,Espresso,HouseBlend是ConcreteComponent。Mocha,Soy,Whip是ConcreteDecorator。
代码示例: Beverage.java
package net.dp.decorator;
public abstract class Beverage {
protected String description = "Unknown Beverage";
public String getDescription() {
return description;
}
public abstract double cost();
}
CondimentDecorator.java
package net.dp.decorator;
public abstract class CondimentDecorator extends Beverage {
public abstract String getDescription();
}
DarkRoast.java
package net.dp.decorator.coffee;
import net.dp.decorator.Beverage;
public class DarkRoast extends Beverage {
public DarkRoast() {
description = "DarkRoast";
}
public double cost() {
return .99;
}
}
Espresso.java
package net.dp.decorator.coffee;
import net.dp.decorator.Beverage;
public class Espresso extends Beverage {
public Espresso() {
description = "Espresso";
}
public double cost() {
return 1.99;
}
}
HouseBlend.java
package net.dp.decorator.coffee;
import net.dp.decorator.Beverage;
public class HouseBlend extends Beverage {
public HouseBlend() {
description = "House Blend Coffee";
}
public double cost() {
return .89;
}
}
Mocha.java
package net.dp.decorator.flovoring;
import net.dp.decorator.Beverage;
import net.dp.decorator.CondimentDecorator;
public class Mocha extends CondimentDecorator {
Beverage beverage;
public Mocha(Beverage beverage) {
this.beverage = beverage;
}
public String getDescription() {
return beverage.getDescription() + ", Mocha";
}
public double cost() {
return .20 + beverage.cost();
}
}
Soy.java
package net.dp.decorator.flovoring;
import net.dp.decorator.Beverage;
import net.dp.decorator.CondimentDecorator;
public class Soy extends CondimentDecorator {
Beverage beverage;
public Soy(Beverage beverage) {
this.beverage = beverage;
}
public String getDescription() {
return beverage.getDescription() + ", Soy";
}
public double cost() {
return .15 + beverage.cost();
}
}
Whip.java
package net.dp.decorator.flovoring;
import net.dp.decorator.Beverage;
import net.dp.decorator.CondimentDecorator;
public class Whip extends CondimentDecorator {
Beverage beverage;
public Whip(Beverage beverage) {
this.beverage = beverage;
}
public String getDescription() {
return beverage.getDescription() + ", Whip";
}
public double cost() {
return .10 + beverage.cost();
}
}
StarbuzzCoffee.java
package net.dp.decorator;
import net.dp.decorator.coffee.DarkRoast;
import net.dp.decorator.coffee.Espresso;
import net.dp.decorator.coffee.HouseBlend;
import net.dp.decorator.flovoring.Mocha;
import net.dp.decorator.flovoring.Soy;
import net.dp.decorator.flovoring.Whip;
public class StarbuzzCoffee {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Beverage beverage = new Espresso();
System.out.println(beverage.getDescription() + " $" + beverage.cost());
Beverage beverage2 = new DarkRoast();
beverage2 = new Mocha(beverage2);
beverage2 = new Mocha(beverage2);
beverage2 = new Whip(beverage2);
System.out.println(beverage2.getDescription() + " $" + beverage2.cost());
Beverage beverage3 = new HouseBlend();
beverage3 = new Whip(new Mocha(new Soy(beverage3)));
System.out.println(beverage3.getDescription() + " $" + beverage3.cost());
}
}
在StarbuzzCoffee中,首先展示不使用装饰者的情形。紧接着是一种装饰者模式的使用,用两个Mocha和一个Whip对象来包装DarkRoast对象。最后一种是更为常见的调用方式,最里层的是ConcreteComponent,外层的都是ConcreteDecorator,可以一直这样包装下去。
4. 工厂模式
4.1 简单工厂模式
工厂处理创建对象的细节。定义简单工厂。
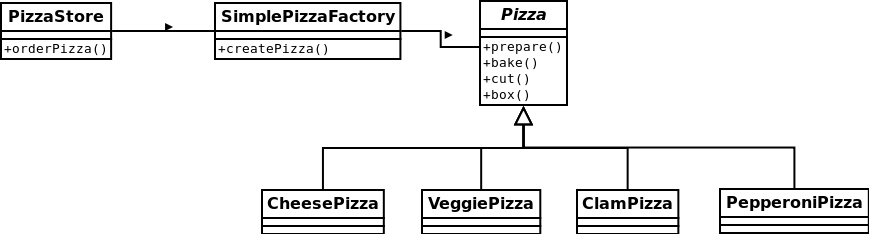
在PizzaStore中把创建Pizza对象的代码逻辑抽出,使用简单工厂来创建相应对象。
package net.dp.factory.simpleFactory;
public class PizzaStore {
SimplePizzaFactory factory;
public PizzaStore(SimplePizzaFactory factory) {
this.factory = factory;
}
public Pizza orderPizza(String type) {
Pizza pizza;
pizza = factory.createPizza(type);
pizza.prepare();
pizza.bake();
pizza.cut();
pizza.box();
return pizza;
}
}
简单工厂通过参数确定需要创建的Pizza对象类型。
package net.dp.factory.simpleFactory;
public class SimplePizzaFactory {
public Pizza createPizza(String type) {
Pizza pizza = null;
if (type.equals("cheese")) {
pizza = new CheesePizza();
} else if (type.equals("pepperoni")) {
pizza = new PepperoniPizza();
} else if (type.equals("clam")) {
pizza = new ClamPizza();
} else if (type.equals("veggie")) {
pizza = new VeggiePizza();
}
return pizza;
}
}
Pizza基类。
package net.dp.factory.simpleFactory;
import java.util.ArrayList;
abstract public class Pizza {
String name;
String dough;
String sauce;
ArrayList<String> toppings = new ArrayList<String>();
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void prepare() {
System.out.println("Preparing " + name);
}
public void bake() {
System.out.println("Baking " + name);
}
public void cut() {
System.out.println("Cutting " + name);
}
public void box() {
System.out.println("Boxing " + name);
}
public String toString() {
// code to display pizza name and ingredients
StringBuffer display = new StringBuffer();
display.append("---- " + name + " ----\n");
display.append(dough + "\n");
display.append(sauce + "\n");
for (int i = 0; i < toppings.size(); i++) {
display.append(toppings.get(i) + "\n");
}
return display.toString();
}
}
Pizza子类。
CheesePizza.java
package net.dp.factory.simpleFactory;
public class CheesePizza extends Pizza {
public CheesePizza() {
name = "Cheese Pizza";
dough = "Regular Crust";
sauce = "Marinara Pizza Sauce";
toppings.add("Fresh Mozzarella");
toppings.add("Parmesan");
}
}
VeggiePizza.java
package net.dp.factory.simpleFactory;
public class VeggiePizza extends Pizza {
public VeggiePizza() {
name = "Veggie Pizza";
dough = "Crust";
sauce = "Marinara sauce";
toppings.add("Shredded mozzarella");
toppings.add("Grated parmesan");
toppings.add("Diced onion");
toppings.add("Sliced mushrooms");
toppings.add("Sliced red pepper");
toppings.add("Sliced black olives");
}
}
PepperoniPizza.java
package net.dp.factory.simpleFactory;
public class PepperoniPizza extends Pizza {
public PepperoniPizza() {
name = "Pepperoni Pizza";
dough = "Crust";
sauce = "Marinara sauce";
toppings.add("Sliced Pepperoni");
toppings.add("Sliced Onion");
toppings.add("Grated parmesan cheese");
}
}
ClamPizza.java
package net.dp.factory.simpleFactory;
public class ClamPizza extends Pizza {
public ClamPizza() {
name = "Clam Pizza";
dough = "Thin crust";
sauce = "White garlic sauce";
toppings.add("Clams");
toppings.add("Grated parmesan cheese");
}
}
调用时,通过给简单工厂对象传递需要的Pizza参数名,完成子类Pizza对象的创建。
PizzaTestDrive.java
package net.dp.factory.simpleFactory;
public class PizzaTestDrive {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SimplePizzaFactory factory = new SimplePizzaFactory();
PizzaStore store = new PizzaStore(factory);
Pizza pizza = store.orderPizza("cheese");
System.out.println("We ordered a " + pizza.getName() + "\n");
pizza = store.orderPizza("veggie");
System.out.println("We ordered a " + pizza.getName() + "\n");
}
}
简单工厂有个明显的问题,制作pizza的过程代码绑在PizzaStore里。
4.2 工厂方法模式
简单工厂有个明显的问题,制作pizza的过程代码绑在PizzaStore里。工厂方法模式可以解决这个问题。它将如何制作Pizza的过程交给子类做决定。在基类中提供抽象接口。
工厂方法模式-定义了创建对象的接口,但由子类决定要实例化的类是哪一个。工厂方法让类把实例化推迟到子类。
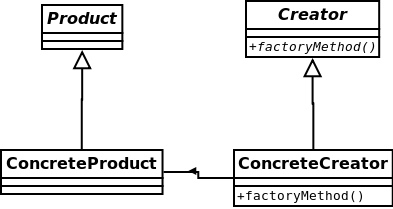
转换成PizzaStore的例子。
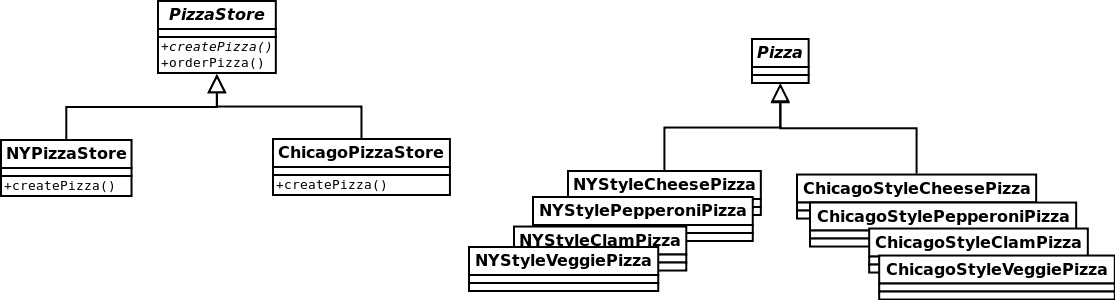
设计原则-要依赖抽象,不要依赖具体类(依赖倒置原则)。不能让高层组件依赖低层组件,而且,不管高层或低层组件,“两者”都应该依赖于抽象。所谓“高层”组件,是由其他低层组件定义其行为的类。例如,PizzaStore是个高层组件,因为它的行为是由Pizza定义的:PizzaStore创建所有不同的Pizza对象,准备、烘烤、切片、装盒;而Pizza本身属于低层组件。
几个原则可以避免在OO设计中违反依赖倒置原则:
- 变量不可以持有具体类的引用。
- 不要让类派生自具体类。
- 不要覆盖基类中已实现的方法。
代码示例: PizzaStore通过方法createPizza()将产生对象推迟到子类中进行。
package net.dp.factory.factoryMethod;
public abstract class PizzaStore {
abstract Pizza createPizza(String item);
public Pizza orderPizza(String type) {
Pizza pizza = createPizza(type);
System.out.println("--- Making a " + pizza.getName() + " ---");
pizza.prepare();
pizza.bake();
pizza.cut();
pizza.box();
return pizza;
}
}
两个子类工厂NYPizzaStore和ChicagoPizzaStore。
package net.dp.factory.factoryMethod;
public class NYPizzaStore extends PizzaStore {
Pizza createPizza(String item) {
if (item.equals("cheese")) {
return new NYStyleCheesePizza();
} else if (item.equals("veggie")) {
return new NYStyleVeggiePizza();
} else if (item.equals("clam")) {
return new NYStyleClamPizza();
} else if (item.equals("pepperoni")) {
return new NYStylePepperoniPizza();
} else return null;
}
}
package net.dp.factory.factoryMethod;
public class ChicagoPizzaStore extends PizzaStore {
Pizza createPizza(String item) {
if (item.equals("cheese")) {
return new ChicagoStyleCheesePizza();
} else if (item.equals("veggie")) {
return new ChicagoStyleVeggiePizza();
} else if (item.equals("clam")) {
return new ChicagoStyleClamPizza();
} else if (item.equals("pepperoni")) {
return new ChicagoStylePepperoniPizza();
} else return null;
}
}
产品类的基类Pizza。
package net.dp.factory.factoryMethod;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public abstract class Pizza {
String name;
String dough;
String sauce;
ArrayList<String> toppings = new ArrayList<String>();
void prepare() {
System.out.println("Preparing " + name);
System.out.println("Tossing dough...");
System.out.println("Adding sauce...");
System.out.println("Adding toppings: ");
for (int i = 0; i < toppings.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(" " + toppings.get(i));
}
}
void bake() {
System.out.println("Bake for 25 minutes at 350");
}
void cut() {
System.out.println("Cutting the pizza into diagonal slices");
}
void box() {
System.out.println("Place pizza in official PizzaStore box");
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public String toString() {
StringBuffer display = new StringBuffer();
display.append("---- " + name + " ----\n");
display.append(dough + "\n");
display.append(sauce + "\n");
for (int i = 0; i < toppings.size(); i++) {
display.append((String) toppings.get(i) + "\n");
}
return display.toString();
}
}
NYPizzaStore下的四种产品。
package net.dp.factory.factoryMethod;
public class NYStyleClamPizza extends Pizza {
public NYStyleClamPizza() {
name = "NY Style Clam Pizza";
dough = "Thin Crust Dough";
sauce = "Marinara Sauce";
toppings.add("Grated Reggiano Cheese");
toppings.add("Fresh Clams from Long Island Sound");
}
}
package net.dp.factory.factoryMethod;
public class NYStyleVeggiePizza extends Pizza {
public NYStyleVeggiePizza() {
name = "NY Style Veggie Pizza";
dough = "Thin Crust Dough";
sauce = "Marinara Sauce";
toppings.add("Grated Reggiano Cheese");
toppings.add("Garlic");
toppings.add("Onion");
toppings.add("Mushrooms");
toppings.add("Red Pepper");
}
}
package net.dp.factory.factoryMethod;
public class NYStylePepperoniPizza extends Pizza {
public NYStylePepperoniPizza() {
name = "NY Style Pepperoni Pizza";
dough = "Thin Crust Dough";
sauce = "Marinara Sauce";
toppings.add("Grated Reggiano Cheese");
toppings.add("Sliced Pepperoni");
toppings.add("Garlic");
toppings.add("Onion");
toppings.add("Mushrooms");
toppings.add("Red Pepper");
}
}
package net.dp.factory.factoryMethod;
public class NYStyleCheesePizza extends Pizza {
public NYStyleCheesePizza() {
name = "NY Style Sauce and Cheese Pizza";
dough = "Thin Crust Dough";
sauce = "Marinara Sauce";
toppings.add("Grated Reggiano Cheese");
}
}
ChicagoPizzaStorePizzaStore下的四种产品。
package net.dp.factory.factoryMethod;
public class ChicagoStyleVeggiePizza extends Pizza {
public ChicagoStyleVeggiePizza() {
name = "Chicago Deep Dish Veggie Pizza";
dough = "Extra Thick Crust Dough";
sauce = "Plum Tomato Sauce";
toppings.add("Shredded Mozzarella Cheese");
toppings.add("Black Olives");
toppings.add("Spinach");
toppings.add("Eggplant");
}
void cut() {
System.out.println("Cutting the pizza into square slices");
}
}
package net.dp.factory.factoryMethod;
public class ChicagoStylePepperoniPizza extends Pizza {
public ChicagoStylePepperoniPizza() {
name = "Chicago Style Pepperoni Pizza";
dough = "Extra Thick Crust Dough";
sauce = "Plum Tomato Sauce";
toppings.add("Shredded Mozzarella Cheese");
toppings.add("Black Olives");
toppings.add("Spinach");
toppings.add("Eggplant");
toppings.add("Sliced Pepperoni");
}
void cut() {
System.out.println("Cutting the pizza into square slices");
}
}
package net.dp.factory.factoryMethod;
public class ChicagoStyleClamPizza extends Pizza {
public ChicagoStyleClamPizza() {
name = "Chicago Style Clam Pizza";
dough = "Extra Thick Crust Dough";
sauce = "Plum Tomato Sauce";
toppings.add("Shredded Mozzarella Cheese");
toppings.add("Frozen Clams from Chesapeake Bay");
}
void cut() {
System.out.println("Cutting the pizza into square slices");
}
}
package net.dp.factory.factoryMethod;
public class ChicagoStyleCheesePizza extends Pizza {
public ChicagoStyleCheesePizza() {
name = "Chicago Style Deep Dish Cheese Pizza";
dough = "Extra Thick Crust Dough";
sauce = "Plum Tomato Sauce";
toppings.add("Shredded Mozzarella Cheese");
}
void cut() {
System.out.println("Cutting the pizza into square slices");
}
}
创建两个子类工厂示例,并指定相应的产品参数,可以实例化所需要的产品。
package net.dp.factory.factoryMethod;
public class PizzaTestDrive {
public static void main(String[] args) {
PizzaStore nyStore = new NYPizzaStore();
PizzaStore chicagoStore = new ChicagoPizzaStore();
Pizza pizza = nyStore.orderPizza("cheese");
System.out.println("Ethan ordered a " + pizza.getName() + "\n");
pizza = chicagoStore.orderPizza("cheese");
System.out.println("Joel ordered a " + pizza.getName() + "\n");
pizza = nyStore.orderPizza("clam");
System.out.println("Ethan ordered a " + pizza.getName() + "\n");
pizza = chicagoStore.orderPizza("clam");
System.out.println("Joel ordered a " + pizza.getName() + "\n");
pizza = nyStore.orderPizza("pepperoni");
System.out.println("Ethan ordered a " + pizza.getName() + "\n");
pizza = chicagoStore.orderPizza("pepperoni");
System.out.println("Joel ordered a " + pizza.getName() + "\n");
pizza = nyStore.orderPizza("veggie");
System.out.println("Ethan ordered a " + pizza.getName() + "\n");
pizza = chicagoStore.orderPizza("veggie");
System.out.println("Joel ordered a " + pizza.getName() + "\n");
}
}
4.3 抽象工厂模式
抽象工厂模式-提供一个接口,用于创建相关或依赖对象的家族,而不需要明确指定具体类。
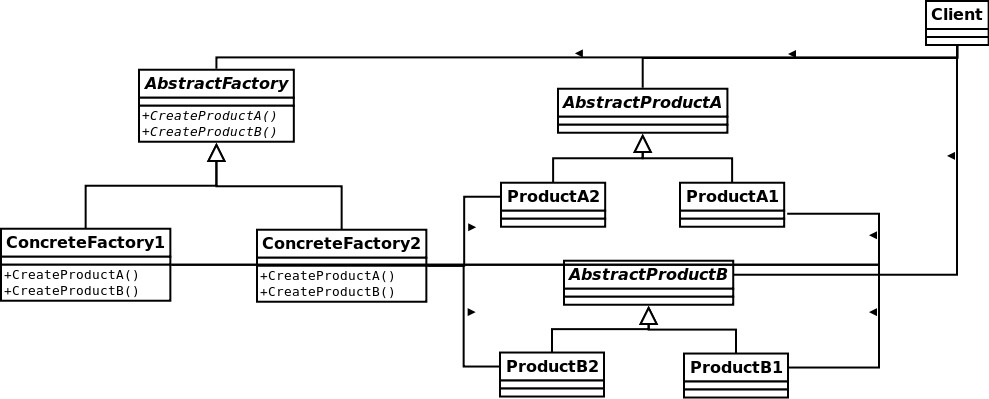
比较工厂方法模式和抽象工厂模式。工厂方法模式是通过子类来创建对象。用这种做法,客户只需要知道他们所使用的抽象类型就可以了,而由子类来负责决定具体类型。抽象工厂提供一个用来创建一个产品家族的抽象类型,这个类型的子类定义了产品被生产的方法。要想使用这个工厂,必须先实例化它,然后将它传入一些针对抽象类型所写的代码中。
代码示例: 原料工厂基类PizzaIngredientFactory(相当于AbstractFactory)
package net.dp.factory.abstractFactory;
public interface PizzaIngredientFactory {
public Dough createDough();
public Sauce createSauce();
public Cheese createCheese();
public Veggies[] createVeggies();
public Pepperoni createPepperoni();
public Clams createClam();
}
两个原料工厂子类NYPizzaIngredientFactory和ChicagoPizzaIngredientFactory(相当于ConcreteFactory)
package net.dp.factory.abstractFactory;
public class NYPizzaIngredientFactory implements PizzaIngredientFactory {
public Dough createDough() {
return new ThinCrustDough();
}
public Sauce createSauce() {
return new MarinaraSauce();
}
public Cheese createCheese() {
return new ReggianoCheese();
}
public Veggies[] createVeggies() {
Veggies veggies[] = { new Garlic(), new Onion(), new Mushroom(), new RedPepper() };
return veggies;
}
public Pepperoni createPepperoni() {
return new SlicedPepperoni();
}
public Clams createClam() {
return new FreshClams();
}
}
package net.dp.factory.abstractFactory;
public class NYPizzaIngredientFactory implements PizzaIngredientFactory {
public Dough createDough() {
return new ThinCrustDough();
}
public Sauce createSauce() {
return new MarinaraSauce();
}
public Cheese createCheese() {
return new ReggianoCheese();
}
public Veggies[] createVeggies() {
Veggies veggies[] = { new Garlic(), new Onion(), new Mushroom(), new RedPepper() };
return veggies;
}
public Pepperoni createPepperoni() {
return new SlicedPepperoni();
}
public Clams createClam() {
return new FreshClams();
}
}
六种原料产品基类Dough、Sauce、Cheese、Clams、Veggies、Pepperoni
package net.dp.factory.abstractFactory;
public interface Dough {
public String toString();
package net.dp.factory.abstractFactory;
public interface Sauce {
public String toString();
}
package net.dp.factory.abstractFactory;
public interface Cheese {
public String toString();
}
package net.dp.factory.abstractFactory;
public interface Clams {
public String toString();
}
package net.dp.factory.abstractFactory;
public interface Veggies {
public String toString();
}
package net.dp.factory.abstractFactory;
public interface Pepperoni {
public String toString();
}
与上面六种产品基类对应的两组具体原料产品簇
- ThickCrustDough和ThinCrustDough对应Dough
- PlumTomatoSauce和MarinaraSauce对应Sauce
- MozzarellaCheese和ReggianoCheese对应Cheese
- FreshClams和FrozenClams对应Clams
- Garlic, Onion, Mushroom, RedPepper和BlackOlives, Spinach, Eggplant对应Veggies
- SlicedPepperoni对应Pepperoni
产品工厂基类PizzaStore,把产品的生产延迟到子类进行(工厂方法)
package net.dp.factory.abstractFactory;
public abstract class PizzaStore {
protected abstract Pizza createPizza(String item);
public Pizza orderPizza(String type) {
Pizza pizza = createPizza(type);
System.out.println("--- Making a " + pizza.getName() + " ---");
pizza.prepare();
pizza.bake();
pizza.cut();
pizza.box();
return pizza;
}
}
产品工厂子类NYPizzaStore和ChicagoPizzaStore
package net.dp.factory.abstractFactory;
public class NYPizzaStore extends PizzaStore {
protected Pizza createPizza(String item) {
Pizza pizza = null;
PizzaIngredientFactory ingredientFactory =
new NYPizzaIngredientFactory();
if (item.equals("cheese")) {
pizza = new CheesePizza(ingredientFactory);
pizza.setName("New York Style Cheese Pizza");
} else if (item.equals("veggie")) {
pizza = new VeggiePizza(ingredientFactory);
pizza.setName("New York Style Veggie Pizza");
} else if (item.equals("clam")) {
pizza = new ClamPizza(ingredientFactory);
pizza.setName("New York Style Clam Pizza");
} else if (item.equals("pepperoni")) {
pizza = new PepperoniPizza(ingredientFactory);
pizza.setName("New York Style Pepperoni Pizza");
}
return pizza;
}
}
package net.dp.factory.abstractFactory;
public class ChicagoPizzaStore extends PizzaStore {
protected Pizza createPizza(String item) {
Pizza pizza = null;
PizzaIngredientFactory ingredientFactory =
new ChicagoPizzaIngredientFactory();
if (item.equals("cheese")) {
pizza = new CheesePizza(ingredientFactory);
pizza.setName("Chicago Style Cheese Pizza");
} else if (item.equals("veggie")) {
pizza = new VeggiePizza(ingredientFactory);
pizza.setName("Chicago Style Veggie Pizza");
} else if (item.equals("clam")) {
pizza = new ClamPizza(ingredientFactory);
pizza.setName("Chicago Style Clam Pizza");
} else if (item.equals("pepperoni")) {
pizza = new PepperoniPizza(ingredientFactory);
pizza.setName("Chicago Style Pepperoni Pizza");
}
return pizza;
}
}
产品基类
package net.dp.factory.abstractFactory;
public abstract class Pizza {
String name;
Dough dough;
Sauce sauce;
Veggies veggies[];
Cheese cheese;
Pepperoni pepperoni;
Clams clam;
abstract void prepare();
void bake() {
System.out.println("Bake for 25 minutes at 350");
}
void cut() {
System.out.println("Cutting the pizza into diagonal slices");
}
void box() {
System.out.println("Place pizza in official PizzaStore box");
}
void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
String getName() {
return name;
}
public String toString() {
StringBuffer result = new StringBuffer();
result.append("---- " + name + " ----\n");
if (dough != null) {
result.append(dough);
result.append("\n");
}
if (sauce != null) {
result.append(sauce);
result.append("\n");
}
if (cheese != null) {
result.append(cheese);
result.append("\n");
}
if (veggies != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < veggies.length; i++) {
result.append(veggies[i]);
if (i < veggies.length-1) {
result.append(", ");
}
}
result.append("\n");
}
if (clam != null) {
result.append(clam);
result.append("\n");
}
if (pepperoni != null) {
result.append(pepperoni);
result.append("\n");
}
return result.toString();
}
}
四种产品子类,这里相当于把原料产品的生产延迟到子类(使用的是工厂方法模式)
package net.dp.factory.abstractFactory;
public class CheesePizza extends Pizza {
PizzaIngredientFactory ingredientFactory;
public CheesePizza(PizzaIngredientFactory ingredientFactory) {
this.ingredientFactory = ingredientFactory;
}
void prepare() {
System.out.println("Preparing " + name);
dough = ingredientFactory.createDough();
sauce = ingredientFactory.createSauce();
cheese = ingredientFactory.createCheese();
}
}
package net.dp.factory.abstractFactory;
public class ClamPizza extends Pizza {
PizzaIngredientFactory ingredientFactory;
public ClamPizza(PizzaIngredientFactory ingredientFactory) {
this.ingredientFactory = ingredientFactory;
}
void prepare() {
System.out.println("Preparing " + name);
dough = ingredientFactory.createDough();
sauce = ingredientFactory.createSauce();
cheese = ingredientFactory.createCheese();
clam = ingredientFactory.createClam();
}
}
package net.dp.factory.abstractFactory;
public class VeggiePizza extends Pizza {
PizzaIngredientFactory ingredientFactory;
public VeggiePizza(PizzaIngredientFactory ingredientFactory) {
this.ingredientFactory = ingredientFactory;
}
void prepare() {
System.out.println("Preparing " + name);
dough = ingredientFactory.createDough();
sauce = ingredientFactory.createSauce();
cheese = ingredientFactory.createCheese();
veggies = ingredientFactory.createVeggies();
}
}
package net.dp.factory.abstractFactory;
public class PepperoniPizza extends Pizza {
PizzaIngredientFactory ingredientFactory;
public PepperoniPizza(PizzaIngredientFactory ingredientFactory) {
this.ingredientFactory = ingredientFactory;
}
void prepare() {
System.out.println("Preparing " + name);
dough = ingredientFactory.createDough();
sauce = ingredientFactory.createSauce();
cheese = ingredientFactory.createCheese();
veggies = ingredientFactory.createVeggies();
pepperoni = ingredientFactory.createPepperoni();
}
}
最终的调用方式
package net.dp.factory.abstractFactory;
public class PizzaTestDrive {
public static void main(String[] args) {
PizzaStore nyStore = new NYPizzaStore();
PizzaStore chicagoStore = new ChicagoPizzaStore();
Pizza pizza = nyStore.orderPizza("cheese");
System.out.println("Ethan ordered a " + pizza + "\n");
pizza = chicagoStore.orderPizza("cheese");
System.out.println("Joel ordered a " + pizza + "\n");
pizza = nyStore.orderPizza("clam");
System.out.println("Ethan ordered a " + pizza + "\n");
pizza = chicagoStore.orderPizza("clam");
System.out.println("Joel ordered a " + pizza + "\n");
pizza = nyStore.orderPizza("pepperoni");
System.out.println("Ethan ordered a " + pizza + "\n");
pizza = chicagoStore.orderPizza("pepperoni");
System.out.println("Joel ordered a " + pizza + "\n");
pizza = nyStore.orderPizza("veggie");
System.out.println("Ethan ordered a " + pizza + "\n");
pizza = chicagoStore.orderPizza("veggie");
System.out.println("Joel ordered a " + pizza + "\n");
}
}
5.单例模式(单件模式)
单例模式-确保一个类只有一个实例,并提供一个全局访问点。

经典单例模式,采用“延迟初始化(lazy instantiaze)”,只在第一次申请对象时,才初始化对象。
package net.dp.singleton.classic;
//NOTE: This is not thread safe!
public class Singleton {
private static Singleton uniqueInstance;
// other useful instance variables here
private Singleton() {
}
public static Singleton getInstance() {
if (uniqueInstance == null) {
uniqueInstance = new Singleton();
}
return uniqueInstance;
}
// other useful methods here
}
上面的例子,在多线程环境下会出现问题,简单的决绝方法是使用”急切初始化(eager instantiaze)”
package net.dp.singleton.threadsafe.eager;
public class Singleton {
private static Singleton uniqueInstance = new Singleton();
private Singleton() {
}
public static Singleton getInstance() {
return uniqueInstance;
}
}
但是如果创建一个实例是需要消耗大量资源,并且它并不是每次都被使用,或者会在程序的后期才被使用到,则上面的方法效率不高。可以利用“双重检查加锁(double-checked locking)”,在第一次检查没有创建实例时,才进行同步,此时再次检查是否有创建对象,如果还是没有,则创建之。这样的做法在JDK5及其后续版本中是有效的。
package net.dp.singleton.threadsafe.dcl;
//double-checked locking
//Danger! This implementation of Singleton not
//guaranteed to work prior to Java 5
public class Singleton {
private volatile static Singleton uniqueInstance;
private Singleton() {
}
public static Singleton getInstance() {
if (uniqueInstance == null) {
synchronized (Singleton.class) {
if (uniqueInstance == null) {
uniqueInstance = new Singleton();
}
}
}
return uniqueInstance;
}
}
6.命令模式-封装调用
命令模式-将“请求”封装成对象,以便使用不同的请求、队列或日志来参数化其他对象。命令模式也支持可撤销的操作。
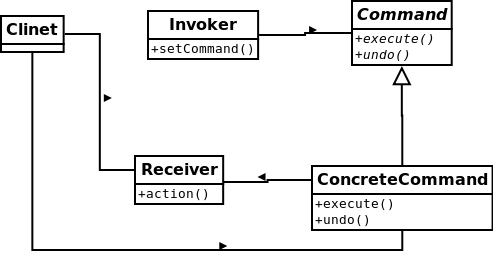
命令模式代码示例: Command接口
package net.dp.command.simpleremote;
public interface Command {
public void execute();
}
所要封装的两个事物GarageDoor和Light(Receiver)
package net.dp.command.simpleremote;
public class GarageDoor {
public GarageDoor() {
}
public void up() {
System.out.println("Garage Door is Open");
}
public void down() {
System.out.println("Garage Door is Closed");
}
public void stop() {
System.out.println("Garage Door is Stopped");
}
public void lightOn() {
System.out.println("Garage light is on");
}
public void lightOff() {
System.out.println("Garage light is off");
}
}
package net.dp.command.simpleremote;
public class Light {
public Light() {
}
public void on() {
System.out.println("Light is on");
}
public void off() {
System.out.println("Light is off");
}
}
封装的具体命令(ConcreteCommand)
package net.dp.command.simpleremote;
public class GarageDoorOpenCommand implements Command {
GarageDoor garageDoor;
public GarageDoorOpenCommand(GarageDoor garageDoor) {
this.garageDoor = garageDoor;
}
public void execute() {
garageDoor.up();
}
}
package net.dp.command.simpleremote;
public class LightOnCommand implements Command {
Light light;
public LightOnCommand(Light light) {
this.light = light;
}
public void execute() {
light.on();
}
}
package net.dp.command.simpleremote;
public class LightOffCommand implements Command {
Light light;
public LightOffCommand(Light light) {
this.light = light;
}
public void execute() {
light.off();
}
}
下面是Invoker
package net.dp.command.simpleremote;
//
// This is the invoker
//
public class SimpleRemoteControl {
Command slot;
public SimpleRemoteControl() {}
public void setCommand(Command command) {
slot = command;
}
public void buttonWasPressed() {
slot.execute();
}
}
调用关系
package net.dp.command.simpleremote;
public class RemoteControlTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SimpleRemoteControl remote = new SimpleRemoteControl();
Light light = new Light();
GarageDoor garageDoor = new GarageDoor();
LightOnCommand lightOn = new LightOnCommand(light);
GarageDoorOpenCommand garageOpen = new GarageDoorOpenCommand(garageDoor);
remote.setCommand(lightOn);
remote.buttonWasPressed();
remote.setCommand(garageOpen);
remote.buttonWasPressed();
}
}
下面是带有undo功能的命令模式示例 Command接口
package net.dp.command.undo;
public interface Command {
public void execute();
public void undo();
}
所要封装的两个事物CeilingFan和Light(Receiver)
package net.dp.command.undo;
public class CeilingFan {
public static final int HIGH = 3;
public static final int MEDIUM = 2;
public static final int LOW = 1;
public static final int OFF = 0;
String location;
int speed;
public CeilingFan(String location) {
this.location = location;
speed = OFF;
}
public void high() {
speed = HIGH;
System.out.println(location + " ceiling fan is on high");
}
public void medium() {
speed = MEDIUM;
System.out.println(location + " ceiling fan is on medium");
}
public void low() {
speed = LOW;
System.out.println(location + " ceiling fan is on low");
}
public void off() {
speed = OFF;
System.out.println(location + " ceiling fan is off");
}
public int getSpeed() {
return speed;
}
}
package net.dp.command.undo;
public class Light {
String location;
int level;
public Light(String location) {
this.location = location;
}
public void on() {
level = 100;
System.out.println("Light is on");
}
public void off() {
level = 0;
System.out.println("Light is off");
}
public void dim(int level) {
this.level = level;
if (level == 0) {
off();
}
else {
System.out.println("Light is dimmed to " + level + "%");
}
}
public int getLevel() {
return level;
}
}
封装的具体命令(ConcreteCommand)
这里为了实现undo(),在execute()执行之前,会保存之前的对象状态。
package net.dp.command.undo;
public class CeilingFanHighCommand implements Command {
CeilingFan ceilingFan;
int prevSpeed;
public CeilingFanHighCommand(CeilingFan ceilingFan) {
this.ceilingFan = ceilingFan;
}
public void execute() {
prevSpeed = ceilingFan.getSpeed();
ceilingFan.high();
}
public void undo() {
if (prevSpeed == CeilingFan.HIGH) {
ceilingFan.high();
} else if (prevSpeed == CeilingFan.MEDIUM) {
ceilingFan.medium();
} else if (prevSpeed == CeilingFan.LOW) {
ceilingFan.low();
} else if (prevSpeed == CeilingFan.OFF) {
ceilingFan.off();
}
}
}
package net.dp.command.undo;
public class CeilingFanMediumCommand implements Command {
CeilingFan ceilingFan;
int prevSpeed;
public CeilingFanMediumCommand(CeilingFan ceilingFan) {
this.ceilingFan = ceilingFan;
}
public void execute() {
prevSpeed = ceilingFan.getSpeed();
ceilingFan.medium();
}
public void undo() {
if (prevSpeed == CeilingFan.HIGH) {
ceilingFan.high();
} else if (prevSpeed == CeilingFan.MEDIUM) {
ceilingFan.medium();
} else if (prevSpeed == CeilingFan.LOW) {
ceilingFan.low();
} else if (prevSpeed == CeilingFan.OFF) {
ceilingFan.off();
}
}
}
package net.dp.command.undo;
public class CeilingFanLowCommand implements Command {
CeilingFan ceilingFan;
int prevSpeed;
public CeilingFanLowCommand(CeilingFan ceilingFan) {
this.ceilingFan = ceilingFan;
}
public void execute() {
prevSpeed = ceilingFan.getSpeed();
ceilingFan.low();
}
public void undo() {
if (prevSpeed == CeilingFan.HIGH) {
ceilingFan.high();
} else if (prevSpeed == CeilingFan.MEDIUM) {
ceilingFan.medium();
} else if (prevSpeed == CeilingFan.LOW) {
ceilingFan.low();
} else if (prevSpeed == CeilingFan.OFF) {
ceilingFan.off();
}
}
}
package net.dp.command.undo;
public class CeilingFanOnCommand implements Command {
CeilingFan ceilingFan;
public CeilingFanOnCommand(CeilingFan ceilingFan) {
this.ceilingFan = ceilingFan;
}
public void execute() {
ceilingFan.high();
}
public void undo() {
ceilingFan.off();
}
}
package net.dp.command.undo;
public class CeilingFanOffCommand implements Command {
CeilingFan ceilingFan;
int prevSpeed;
public CeilingFanOffCommand(CeilingFan ceilingFan) {
this.ceilingFan = ceilingFan;
}
public void execute() {
prevSpeed = ceilingFan.getSpeed();
ceilingFan.off();
}
public void undo() {
if (prevSpeed == CeilingFan.HIGH) {
ceilingFan.high();
} else if (prevSpeed == CeilingFan.MEDIUM) {
ceilingFan.medium();
} else if (prevSpeed == CeilingFan.LOW) {
ceilingFan.low();
} else if (prevSpeed == CeilingFan.OFF) {
ceilingFan.off();
}
}
}
package net.dp.command.undo;
public class DimmerLightOnCommand implements Command {
Light light;
int prevLevel;
public DimmerLightOnCommand(Light light) {
this.light = light;
}
public void execute() {
prevLevel = light.getLevel();
light.dim(75);
}
public void undo() {
light.dim(prevLevel);
}
}
package net.dp.command.undo;
public class DimmerLightOffCommand implements Command {
Light light;
int prevLevel;
public DimmerLightOffCommand(Light light) {
this.light = light;
prevLevel = 100;
}
public void execute() {
prevLevel = light.getLevel();
light.off();
}
public void undo() {
light.dim(prevLevel);
}
}
package net.dp.command.undo;
public class LightOnCommand implements Command {
Light light;
public LightOnCommand(Light light) {
this.light = light;
}
public void execute() {
light.on();
}
public void undo() {
light.off();
}
}
package net.dp.command.undo;
public class LightOffCommand implements Command {
Light light;
public LightOffCommand(Light light) {
this.light = light;
}
public void execute() {
light.off();
}
public void undo() {
light.on();
}
}
下面是一个空对象(null object)。可以将处理null的责任转移给空对象。举例来说,遥控器不可能一出厂就设置了有意义的命令对象,所以提供了NoCommand对象作为代用品,当调用它的execute()时,它不会做任何事情。
package net.dp.command.undo;
public class NoCommand implements Command {
public void execute() { }
public void undo() { }
}
下面是Invoker
package net.dp.command.undo;
//
// This is the invoker
//
public class RemoteControlWithUndo {
Command[] onCommands;
Command[] offCommands;
Command undoCommand;
public RemoteControlWithUndo() {
onCommands = new Command[7];
offCommands = new Command[7];
Command noCommand = new NoCommand();
for(int i=0;i<7;i++) {
onCommands[i] = noCommand;
offCommands[i] = noCommand;
}
undoCommand = noCommand;
}
public void setCommand(int slot, Command onCommand, Command offCommand) {
onCommands[slot] = onCommand;
offCommands[slot] = offCommand;
}
public void onButtonWasPushed(int slot) {
onCommands[slot].execute();
undoCommand = onCommands[slot];
}
public void offButtonWasPushed(int slot) {
offCommands[slot].execute();
undoCommand = offCommands[slot];
}
public void undoButtonWasPushed() {
undoCommand.undo();
}
public String toString() {
StringBuffer stringBuff = new StringBuffer();
stringBuff.append("\n------ Remote Control -------\n");
for (int i = 0; i < onCommands.length; i++) {
stringBuff.append("[slot " + i + "] " + onCommands[i].getClass().getName()
+ " " + offCommands[i].getClass().getName() + "\n");
}
stringBuff.append("[undo] " + undoCommand.getClass().getName() + "\n");
return stringBuff.toString();
}
}
调用关系
package net.dp.command.undo;
public class RemoteLoader {
public static void main(String[] args) {
RemoteControlWithUndo remoteControl = new RemoteControlWithUndo();
Light livingRoomLight = new Light("Living Room");
LightOnCommand livingRoomLightOn =
new LightOnCommand(livingRoomLight);
LightOffCommand livingRoomLightOff =
new LightOffCommand(livingRoomLight);
remoteControl.setCommand(0, livingRoomLightOn, livingRoomLightOff);
remoteControl.onButtonWasPushed(0);
remoteControl.offButtonWasPushed(0);
System.out.println(remoteControl);
remoteControl.undoButtonWasPushed();
remoteControl.offButtonWasPushed(0);
remoteControl.onButtonWasPushed(0);
System.out.println(remoteControl);
remoteControl.undoButtonWasPushed();
CeilingFan ceilingFan = new CeilingFan("Living Room");
CeilingFanMediumCommand ceilingFanMedium =
new CeilingFanMediumCommand(ceilingFan);
CeilingFanHighCommand ceilingFanHigh =
new CeilingFanHighCommand(ceilingFan);
CeilingFanOffCommand ceilingFanOff =
new CeilingFanOffCommand(ceilingFan);
remoteControl.setCommand(0, ceilingFanMedium, ceilingFanOff);
remoteControl.setCommand(1, ceilingFanHigh, ceilingFanOff);
remoteControl.onButtonWasPushed(0);
remoteControl.offButtonWasPushed(0);
System.out.println(remoteControl);
remoteControl.undoButtonWasPushed();
remoteControl.onButtonWasPushed(1);
System.out.println(remoteControl);
remoteControl.undoButtonWasPushed();
}
}
设置宏命令,可以将部分命令组合在一起依次连续触发或关闭
package net.dp.command.party;
public class MacroCommand implements Command {
Command[] commands;
public MacroCommand(Command[] commands) {
this.commands = commands;
}
public void execute() {
for (int i = 0; i < commands.length; i++) {
commands[i].execute();
}
}
public void undo() {
for (int i = 0; i < commands.length; i++) {
commands[i].undo();
}
}
}
调用关系
package net.dp.command.party;
public class RemoteLoader {
public static void main(String[] args) {
RemoteControl remoteControl = new RemoteControl();
Light light = new Light("Living Room");
TV tv = new TV("Living Room");
Stereo stereo = new Stereo("Living Room");
Hottub hottub = new Hottub();
LightOnCommand lightOn = new LightOnCommand(light);
StereoOnCommand stereoOn = new StereoOnCommand(stereo);
TVOnCommand tvOn = new TVOnCommand(tv);
HottubOnCommand hottubOn = new HottubOnCommand(hottub);
LightOffCommand lightOff = new LightOffCommand(light);
StereoOffCommand stereoOff = new StereoOffCommand(stereo);
TVOffCommand tvOff = new TVOffCommand(tv);
HottubOffCommand hottubOff = new HottubOffCommand(hottub);
Command[] partyOn = { lightOn, stereoOn, tvOn, hottubOn};
Command[] partyOff = { lightOff, stereoOff, tvOff, hottubOff};
MacroCommand partyOnMacro = new MacroCommand(partyOn);
MacroCommand partyOffMacro = new MacroCommand(partyOff);
remoteControl.setCommand(0, partyOnMacro, partyOffMacro);
System.out.println(remoteControl);
System.out.println("--- Pushing Macro On---");
remoteControl.onButtonWasPushed(0);
System.out.println("--- Pushing Macro Off---");
remoteControl.offButtonWasPushed(0);
}
}
7.适配器模式与外观模式-随遇而安
7.1 适配器模式
适配器模式-将一个类的接口,转换成客户期望的另一个接口。适配器让原本不兼容的类可以合作无间。
“对象”适配器
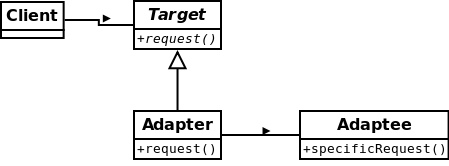
“类”适配器
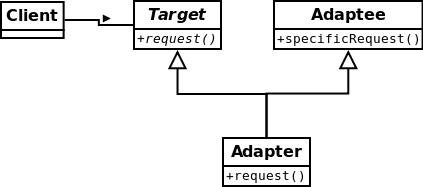
下面展示对象适配器的简单用法。
有两个基类Duck和Turkey
package net.dp.adapter.ducks;
public interface Duck {
public void quack();
public void fly();
}
package net.dp.adapter.ducks;
public interface Turkey {
public void gobble();
public void fly();
}
它们各自有一个子类MallardDuck和WildTurkey
package net.dp.adapter.ducks;
public class MallardDuck implements Duck {
public void quack() {
System.out.println("Quack");
}
public void fly() {
System.out.println("I'm flying");
}
}
package net.dp.adapter.ducks;
public class WildTurkey implements Turkey {
public void gobble() {
System.out.println("Gobble gobble");
}
public void fly() {
System.out.println("I'm flying a short distance");
}
}
现在需要互相适配对方,两个适配器类DuckAdapter和TurkeyAdapter
package net.dp.adapter.ducks;
import java.util.Random;
public class DuckAdapter implements Turkey {
Duck duck;
Random rand;
public DuckAdapter(Duck duck) {
this.duck = duck;
rand = new Random();
}
public void gobble() {
duck.quack();
}
public void fly() {
if (rand.nextInt(5) == 0) {
duck.fly();
}
}
}
package net.dp.adapter.ducks;
public class TurkeyAdapter implements Duck {
Turkey turkey;
public TurkeyAdapter(Turkey turkey) {
this.turkey = turkey;
}
public void quack() {
turkey.gobble();
}
public void fly() {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
turkey.fly();
}
}
}
调用关系
package net.dp.adapter.ducks;
public class DuckTestDrive {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MallardDuck duck = new MallardDuck();
WildTurkey turkey = new WildTurkey();
Duck turkeyAdapter = new TurkeyAdapter(turkey);
System.out.println("The Turkey says...");
turkey.gobble();
turkey.fly();
System.out.println("\nThe Duck says...");
testDuck(duck);
System.out.println("\nThe TurkeyAdapter says...");
testDuck(turkeyAdapter);
}
static void testDuck(Duck duck) {
duck.quack();
duck.fly();
}
}
package net.dp.adapter.ducks;
public class TurkeyTestDrive {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MallardDuck duck = new MallardDuck();
Turkey duckAdapter = new DuckAdapter(duck);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println("The DuckAdapter says...");
duckAdapter.gobble();
duckAdapter.fly();
}
}
}
7.2 外观模式
外观模式-提供了一个统一的接口,用来访问子系统中的一群接口。外观定义了一个高层接口,让子系统更容易使用。这个定义清楚地告诉我们,外观的意图是要提供一个简单的接口,好让一个子系统更易于使用。
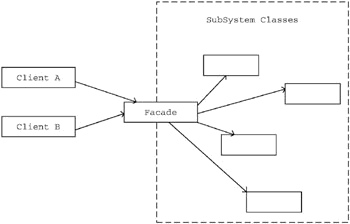
设计原则-最少知识原则:只和你的密友谈话。这个原则希望我们在设计中,不要让太多的类耦合在一起,免得修改系统中的一部分,会影响到其他部分。
代码示例:
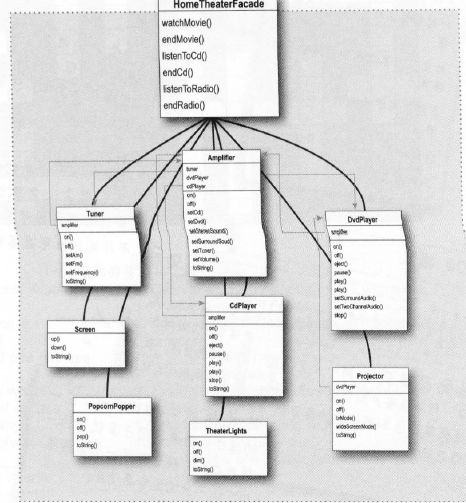
子系统中包含的类有Amplifier,CdPlayer,DvdPlayer,Tuner,Screen,Projector,TheaterLights,PopcomPopper
package net.dp.facade.hometheater;
public class Amplifier {
String description;
Tuner tuner;
DvdPlayer dvd;
CdPlayer cd;
public Amplifier(String description) {
this.description = description;
}
public void on() {
System.out.println(description + " on");
}
public void off() {
System.out.println(description + " off");
}
public void setStereoSound() {
System.out.println(description + " stereo mode on");
}
public void setSurroundSound() {
System.out.println(description + " surround sound on (5 speakers, 1 subwoofer)");
}
public void setVolume(int level) {
System.out.println(description + " setting volume to " + level);
}
public void setTuner(Tuner tuner) {
System.out.println(description + " setting tuner to " + dvd);
this.tuner = tuner;
}
public void setDvd(DvdPlayer dvd) {
System.out.println(description + " setting DVD player to " + dvd);
this.dvd = dvd;
}
public void setCd(CdPlayer cd) {
System.out.println(description + " setting CD player to " + cd);
this.cd = cd;
}
public String toString() {
return description;
}
}
package net.dp.facade.hometheater;
public class CdPlayer {
String description;
int currentTrack;
Amplifier amplifier;
String title;
public CdPlayer(String description, Amplifier amplifier) {
this.description = description;
this.amplifier = amplifier;
}
public void on() {
System.out.println(description + " on");
}
public void off() {
System.out.println(description + " off");
}
public void eject() {
title = null;
System.out.println(description + " eject");
}
public void play(String title) {
this.title = title;
currentTrack = 0;
System.out.println(description + " playing \"" + title + "\"");
}
public void play(int track) {
if (title == null) {
System.out.println(description + " can't play track " + currentTrack +
", no cd inserted");
} else {
currentTrack = track;
System.out.println(description + " playing track " + currentTrack);
}
}
public void stop() {
currentTrack = 0;
System.out.println(description + " stopped");
}
public void pause() {
System.out.println(description + " paused \"" + title + "\"");
}
public String toString() {
return description;
}
}
package net.dp.facade.hometheater;
public class DvdPlayer {
String description;
int currentTrack;
Amplifier amplifier;
String movie;
public DvdPlayer(String description, Amplifier amplifier) {
this.description = description;
this.amplifier = amplifier;
}
public void on() {
System.out.println(description + " on");
}
public void off() {
System.out.println(description + " off");
}
public void eject() {
movie = null;
System.out.println(description + " eject");
}
public void play(String movie) {
this.movie = movie;
currentTrack = 0;
System.out.println(description + " playing \"" + movie + "\"");
}
public void play(int track) {
if (movie == null) {
System.out.println(description + " can't play track " + track + " no dvd inserted");
} else {
currentTrack = track;
System.out.println(description + " playing track " + currentTrack + " of \"" + movie + "\"");
}
}
public void stop() {
currentTrack = 0;
System.out.println(description + " stopped \"" + movie + "\"");
}
public void pause() {
System.out.println(description + " paused \"" + movie + "\"");
}
public void setTwoChannelAudio() {
System.out.println(description + " set two channel audio");
}
public void setSurroundAudio() {
System.out.println(description + " set surround audio");
}
public String toString() {
return description;
}
}
package net.dp.facade.hometheater;
public class Tuner {
String description;
Amplifier amplifier;
double frequency;
public Tuner(String description, Amplifier amplifier) {
this.description = description;
}
public void on() {
System.out.println(description + " on");
}
public void off() {
System.out.println(description + " off");
}
public void setFrequency(double frequency) {
System.out.println(description + " setting frequency to " + frequency);
this.frequency = frequency;
}
public void setAm() {
System.out.println(description + " setting AM mode");
}
public void setFm() {
System.out.println(description + " setting FM mode");
}
public String toString() {
return description;
}
}
package net.dp.facade.hometheater;
public class Screen {
String description;
public Screen(String description) {
this.description = description;
}
public void up() {
System.out.println(description + " going up");
}
public void down() {
System.out.println(description + " going down");
}
public String toString() {
return description;
}
}
package net.dp.facade.hometheater;
public class Projector {
String description;
DvdPlayer dvdPlayer;
public Projector(String description, DvdPlayer dvdPlayer) {
this.description = description;
this.dvdPlayer = dvdPlayer;
}
public void on() {
System.out.println(description + " on");
}
public void off() {
System.out.println(description + " off");
}
public void wideScreenMode() {
System.out.println(description + " in widescreen mode (16x9 aspect ratio)");
}
public void tvMode() {
System.out.println(description + " in tv mode (4x3 aspect ratio)");
}
public String toString() {
return description;
}
}
package net.dp.facade.hometheater;
public class TheaterLights {
String description;
public TheaterLights(String description) {
this.description = description;
}
public void on() {
System.out.println(description + " on");
}
public void off() {
System.out.println(description + " off");
}
public void dim(int level) {
System.out.println(description + " dimming to " + level + "%");
}
public String toString() {
return description;
}
}
package net.dp.facade.hometheater;
public class PopcornPopper {
String description;
public PopcornPopper(String description) {
this.description = description;
}
public void on() {
System.out.println(description + " on");
}
public void off() {
System.out.println(description + " off");
}
public void pop() {
System.out.println(description + " popping popcorn!");
}
public String toString() {
return description;
}
}
提供一个控制子系统的外观类HomeTheaterFacade
package net.dp.facade.hometheater;
public class HomeTheaterFacade {
Amplifier amp;
Tuner tuner;
DvdPlayer dvd;
CdPlayer cd;
Projector projector;
TheaterLights lights;
Screen screen;
PopcornPopper popper;
public HomeTheaterFacade(Amplifier amp,
Tuner tuner,
DvdPlayer dvd,
CdPlayer cd,
Projector projector,
Screen screen,
TheaterLights lights,
PopcornPopper popper) {
this.amp = amp;
this.tuner = tuner;
this.dvd = dvd;
this.cd = cd;
this.projector = projector;
this.screen = screen;
this.lights = lights;
this.popper = popper;
}
public void watchMovie(String movie) {
System.out.println("Get ready to watch a movie...");
popper.on();
popper.pop();
lights.dim(10);
screen.down();
projector.on();
projector.wideScreenMode();
amp.on();
amp.setDvd(dvd);
amp.setSurroundSound();
amp.setVolume(5);
dvd.on();
dvd.play(movie);
}
public void endMovie() {
System.out.println("Shutting movie theater down...");
popper.off();
lights.on();
screen.up();
projector.off();
amp.off();
dvd.stop();
dvd.eject();
dvd.off();
}
public void listenToCd(String cdTitle) {
System.out.println("Get ready for an audiopile experence...");
lights.on();
amp.on();
amp.setVolume(5);
amp.setCd(cd);
amp.setStereoSound();
cd.on();
cd.play(cdTitle);
}
public void endCd() {
System.out.println("Shutting down CD...");
amp.off();
amp.setCd(cd);
cd.eject();
cd.off();
}
public void listenToRadio(double frequency) {
System.out.println("Tuning in the airwaves...");
tuner.on();
tuner.setFrequency(frequency);
amp.on();
amp.setVolume(5);
amp.setTuner(tuner);
}
public void endRadio() {
System.out.println("Shutting down the tuner...");
tuner.off();
amp.off();
}
}
客户端通过外观类来控制子系统
package net.dp.facade.hometheater;
public class HomeTheaterTestDrive {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Amplifier amp = new Amplifier("Top-O-Line Amplifier");
Tuner tuner = new Tuner("Top-O-Line AM/FM Tuner", amp);
DvdPlayer dvd = new DvdPlayer("Top-O-Line DVD Player", amp);
CdPlayer cd = new CdPlayer("Top-O-Line CD Player", amp);
Projector projector = new Projector("Top-O-Line Projector", dvd);
TheaterLights lights = new TheaterLights("Theater Ceiling Lights");
Screen screen = new Screen("Theater Screen");
PopcornPopper popper = new PopcornPopper("Popcorn Popper");
HomeTheaterFacade homeTheater =
new HomeTheaterFacade(amp, tuner, dvd, cd,
projector, screen, lights, popper);
homeTheater.watchMovie("Raiders of the Lost Ark");
homeTheater.endMovie();
}
}
8.模板方法模式-封装算法
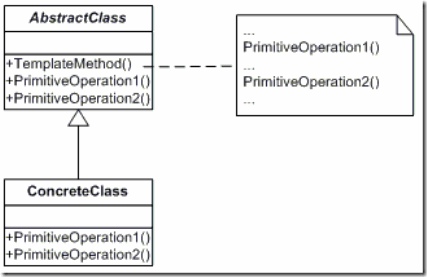
模板方法模式-在一个方法中定义了一个算法的骨架,而将一些步骤延迟到子类中。模板方法使得子类可以在不改变算法结构的情况下,重新定义算法中的某些步骤。
代码示例: 最初的Coffee和Tea两个类设计如下,
package net.dp.templatemethod.simplebarista;
public class Coffee {
void prepareRecipe() {
boilWater();
brewCoffeeGrinds();
pourInCup();
addSugarAndMilk();
}
public void boilWater() {
System.out.println("Boiling water");
}
public void brewCoffeeGrinds() {
System.out.println("Dripping Coffee through filter");
}
public void pourInCup() {
System.out.println("Pouring into cup");
}
public void addSugarAndMilk() {
System.out.println("Adding Sugar and Milk");
}
}
package net.dp.templatemethod.simplebarista;
public class Tea {
void prepareRecipe() {
boilWater();
steepTeaBag();
pourInCup();
addLemon();
}
public void boilWater() {
System.out.println("Boiling water");
}
public void steepTeaBag() {
System.out.println("Steeping the tea");
}
public void addLemon() {
System.out.println("Adding Lemon");
}
public void pourInCup() {
System.out.println("Pouring into cup");
}
}
调用关系
package net.dp.templatemethod.simplebarista;
public class Barista {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Tea tea = new Tea();
Coffee coffee = new Coffee();
System.out.println("Making tea...");
tea.prepareRecipe();
System.out.println("Making coffee...");
coffee.prepareRecipe();
}
}
这里已经观察到Coffee和Tea两个类中存在相同的冲泡逻辑。对其抽象为四个步骤:
- 把水煮沸
- 用热水泡咖啡或茶
- 把饮料倒进杯子
- 在饮料中加入适当的调料
因此,我们把这一算法步骤抽象出来,把共通的部分实现调,不一些不同的步骤定义成抽象方法,使其延迟到子类中去实现。
定义模板方法基类CaffeineBeverage如下,其中共通的部分是boilWater()和pourInCup()。而一些存在变化的方法brew()和addCondiments()则定义成抽象方法。
package net.dp.templatemethod.barista;
public abstract class CaffeineBeverage {
final void prepareRecipe() {
boilWater();
brew();
pourInCup();
addCondiments();
}
abstract void brew();
abstract void addCondiments();
void boilWater() {
System.out.println("Boiling water");
}
void pourInCup() {
System.out.println("Pouring into cup");
}
}
Coffee和Tea两个子类分别继承CaffeineBeverage,实现自己独有的两个步骤。
package net.dp.templatemethod.barista;
public class Coffee extends CaffeineBeverage {
public void brew() {
System.out.println("Dripping Coffee through filter");
}
public void addCondiments() {
System.out.println("Adding Sugar and Milk");
}
}
package net.dp.templatemethod.barista;
public class Tea extends CaffeineBeverage {
public void brew() {
System.out.println("Steeping the tea");
}
public void addCondiments() {
System.out.println("Adding Lemon");
}
}
我们也可以有“默认不做事的方法”,称这些方法为hook(钩子)。当你的子类“必须”提供算法中的某个方法或步骤的实现时,就使用抽象方法。如果算法的这个部分是可选的,就用钩子。下面的模板方法基类CaffeineBeverage定义了一个钩子。
package net.dp.templatemethod.barista;
public abstract class CaffeineBeverageWithHook {
void prepareRecipe() {
boilWater();
brew();
pourInCup();
if (customerWantsCondiments()) {
addCondiments();
}
}
abstract void brew();
abstract void addCondiments();
void boilWater() {
System.out.println("Boiling water");
}
void pourInCup() {
System.out.println("Pouring into cup");
}
boolean customerWantsCondiments() {
return true;
}
}
带有钩子的Coffee和Tea。
package net.dp.templatemethod.barista;
import java.io.*;
public class CoffeeWithHook extends CaffeineBeverageWithHook {
public void brew() {
System.out.println("Dripping Coffee through filter");
}
public void addCondiments() {
System.out.println("Adding Sugar and Milk");
}
public boolean customerWantsCondiments() {
String answer = getUserInput();
if (answer.toLowerCase().startsWith("y")) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
private String getUserInput() {
String answer = null;
System.out.print("Would you like milk and sugar with your coffee (y/n)? ");
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
try {
answer = in.readLine();
} catch (IOException ioe) {
System.err.println("IO error trying to read your answer");
}
if (answer == null) {
return "no";
}
return answer;
}
}
package net.dp.templatemethod.barista;
import java.io.*;
public class TeaWithHook extends CaffeineBeverageWithHook {
public void brew() {
System.out.println("Steeping the tea");
}
public void addCondiments() {
System.out.println("Adding Lemon");
}
public boolean customerWantsCondiments() {
String answer = getUserInput();
if (answer.toLowerCase().startsWith("y")) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
private String getUserInput() {
// get the user's response
String answer = null;
System.out.print("Would you like milk and sugar with your coffee (y/n)? ");
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
try {
answer = in.readLine();
} catch (IOException ioe) {
System.err.println("IO error trying to read your answer");
}
if (answer == null) {
return "no";
}
return answer;
}
}
调用关系。
package net.dp.templatemethod.barista;
public class BeverageTestDrive {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Tea tea = new Tea();
Coffee coffee = new Coffee();
System.out.println("\nMaking tea...");
tea.prepareRecipe();
System.out.println("\nMaking coffee...");
coffee.prepareRecipe();
TeaWithHook teaHook = new TeaWithHook();
CoffeeWithHook coffeeHook = new CoffeeWithHook();
System.out.println("\nMaking tea...");
teaHook.prepareRecipe();
System.out.println("\nMaking coffee...");
coffeeHook.prepareRecipe();
}
}
设计原则-好莱坞原则:别调用(打电话给)我们,我们会调用(打电话给)你。在好莱坞原则之下,我们允许低层组件将自己挂钩到系统上,但是高层组件会决定什么时候和怎样使用这些低层组件。
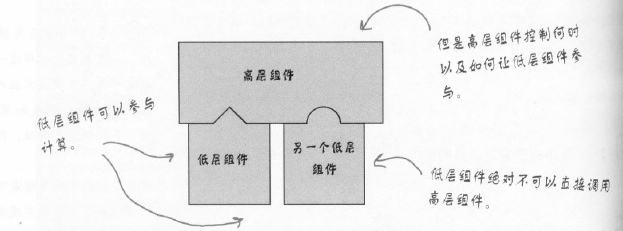
送代器与组合模式-管理良好的集合
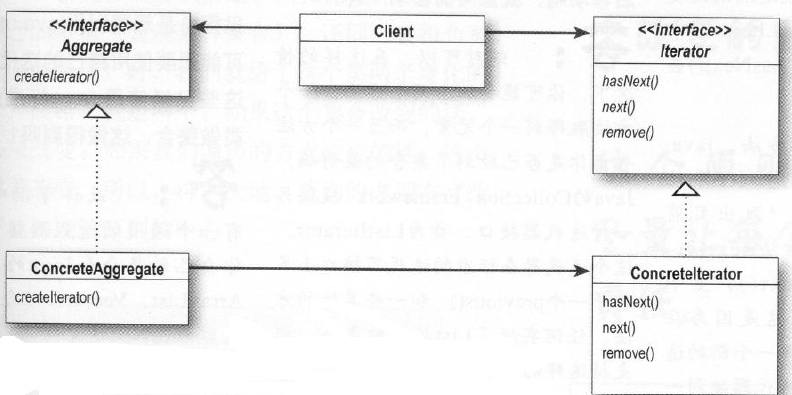
9.1 迭代器模式
迭代器模式-提供一种方法顺序访问一个聚合对象中的各个元素,而又不暴露其内部的表示。迭代器模式让我们能游走于聚合内的每一个元素,而又不暴露其内部的表示。把游走的任务放在迭代器上,而不是聚合上。这样简化了聚合的接口和实现,也让责任各得其所。
设计原则-单一责任。一个类应该只有一个引起变化的原因。类的每个责任都有改变的潜在区域。超过一个责任,意味着超过一个改变的区域。
代码示例:
所有的菜单元素,
package net.dp.iterator.dinermerger;
public class MenuItem {
String name;
String description;
boolean vegetarian;
double price;
public MenuItem(String name, String description, boolean vegetarian,
double price) {
this.name = name;
this.description = description;
this.vegetarian = vegetarian;
this.price = price;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public String getDescription() {
return description;
}
public double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public boolean isVegetarian() {
return vegetarian;
}
public String toString() {
return (name + ", $" + price + "\n " + description);
}
}
定义迭代器接口,
package net.dp.iterator.dinermerger;
public interface Iterator {
boolean hasNext();
Object next();
}
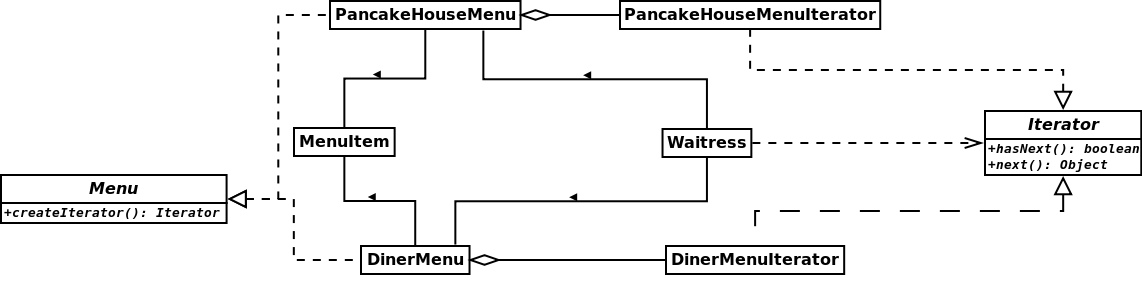
分别有两组菜单,其中PancakeHouseMenu内部数据结构是ArrayList,DinerMenu内部数据结构是数组。它们实现了Menu接口,该接口限定需要创建迭代器实例。
package net.dp.iterator.dinermerger;
public interface Menu {
public Iterator createIterator();
}
package net.dp.iterator.dinermerger;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class PancakeHouseMenu implements Menu {
ArrayList<MenuItem> menuItems;
public PancakeHouseMenu() {
menuItems = new ArrayList<MenuItem>();
addItem("K&B's Pancake Breakfast",
"Pancakes with scrambled eggs, and toast",
true,
2.99);
addItem("Regular Pancake Breakfast",
"Pancakes with fried eggs, sausage",
false,
2.99);
addItem("Blueberry Pancakes",
"Pancakes made with fresh blueberries",
true,
3.49);
addItem("Waffles",
"Waffles, with your choice of blueberries or strawberries",
true,
3.59);
}
public void addItem(String name, String description,
boolean vegetarian, double price)
{
MenuItem menuItem = new MenuItem(name, description, vegetarian, price);
menuItems.add(menuItem);
}
public ArrayList<MenuItem> getMenuItems() {
return menuItems;
}
public Iterator createIterator() {
return new PancakeHouseMenuIterator(menuItems);
}
public String toString() {
return "Objectville Pancake House Menu";
}
// other menu methods here
}
package net.dp.iterator.dinermerger;
public class DinerMenu implements Menu {
static final int MAX_ITEMS = 6;
int numberOfItems = 0;
MenuItem[] menuItems;
public DinerMenu() {
menuItems = new MenuItem[MAX_ITEMS];
addItem("Vegetarian BLT",
"(Fakin') Bacon with lettuce & tomato on whole wheat", true, 2.99);
addItem("BLT",
"Bacon with lettuce & tomato on whole wheat", false, 2.99);
addItem("Soup of the day",
"Soup of the day, with a side of potato salad", false, 3.29);
addItem("Hotdog",
"A hot dog, with saurkraut, relish, onions, topped with cheese",
false, 3.05);
addItem("Steamed Veggies and Brown Rice",
"Steamed vegetables over brown rice", true, 3.99);
addItem("Pasta",
"Spaghetti with Marinara Sauce, and a slice of sourdough bread",
true, 3.89);
}
public void addItem(String name, String description,
boolean vegetarian, double price)
{
MenuItem menuItem = new MenuItem(name, description, vegetarian, price);
if (numberOfItems >= MAX_ITEMS) {
System.err.println("Sorry, menu is full! Can't add item to menu");
} else {
menuItems[numberOfItems] = menuItem;
numberOfItems = numberOfItems + 1;
}
}
public MenuItem[] getMenuItems() {
return menuItems;
}
public Iterator createIterator() {
return new DinerMenuIterator(menuItems);
}
// other menu methods here
}
这两组菜单对应的迭代器,PancakeHouseMenuIterator和DinerMenuIterator,分别对应ArrayList和数据两种内部数据结构。
package net.dp.iterator.dinermerger;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class PancakeHouseMenuIterator implements Iterator {
ArrayList<MenuItem> items;
int position = 0;
public PancakeHouseMenuIterator(ArrayList<MenuItem> items) {
this.items = items;
}
public Object next() {
Object object = items.get(position);
position = position + 1;
return object;
}
public boolean hasNext() {
if (position >= items.size()) {
return false;
} else {
return true;
}
}
}
package net.dp.iterator.dinermerger;
public class DinerMenuIterator implements Iterator {
MenuItem[] items;
int position = 0;
public DinerMenuIterator(MenuItem[] items) {
this.items = items;
}
public Object next() {
MenuItem menuItem = items[position];
position = position + 1;
return menuItem;
}
public boolean hasNext() {
if (position >= items.length || items[position] == null) {
return false;
} else {
return true;
}
}
}
对于Waitress来说,她是通过Iterator来操作这两组菜单中的MenuItem,而对于其内部数据结构是ArrayList还是数组并不知晓。
package net.dp.iterator.dinermerger;
public class Waitress {
PancakeHouseMenu pancakeHouseMenu;
DinerMenu dinerMenu;
public Waitress(PancakeHouseMenu pancakeHouseMenu, DinerMenu dinerMenu) {
this.pancakeHouseMenu = pancakeHouseMenu;
this.dinerMenu = dinerMenu;
}
public void printMenu() {
Iterator pancakeIterator = pancakeHouseMenu.createIterator();
Iterator dinerIterator = dinerMenu.createIterator();
System.out.println("MENU\n----\nBREAKFAST");
printMenu(pancakeIterator);
System.out.println("\nLUNCH");
printMenu(dinerIterator);
}
private void printMenu(Iterator iterator) {
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
MenuItem menuItem = (MenuItem)iterator.next();
System.out.print(menuItem.getName() + ", ");
System.out.print(menuItem.getPrice() + " -- ");
System.out.println(menuItem.getDescription());
}
}
public void printVegetarianMenu() {
printVegetarianMenu(pancakeHouseMenu.createIterator());
printVegetarianMenu(dinerMenu.createIterator());
}
public boolean isItemVegetarian(String name) {
Iterator breakfastIterator = pancakeHouseMenu.createIterator();
if (isVegetarian(name, breakfastIterator)) {
return true;
}
Iterator dinnerIterator = dinerMenu.createIterator();
if (isVegetarian(name, dinnerIterator)) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
private void printVegetarianMenu(Iterator iterator) {
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
MenuItem menuItem = (MenuItem)iterator.next();
if (menuItem.isVegetarian()) {
System.out.print(menuItem.getName());
System.out.println("\t\t" + menuItem.getPrice());
System.out.println("\t" + menuItem.getDescription());
}
}
}
private boolean isVegetarian(String name, Iterator iterator) {
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
MenuItem menuItem = (MenuItem)iterator.next();
if (menuItem.getName().equals(name)) {
if (menuItem.isVegetarian()) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
}
9.2 组合模式
组合模式-允许你将对象组合成树形结构来表现“整体/部分”层次结构。组合能让客户以一致的方式处理个别对象以及对象组合。使用组合结构,我们能把相同的操作应用在组合和个别对象上,换句话说,在大多数情况下,我们可以忽略对象组合和个别对象之间的差别。
利用组合设计菜单,
MenuComponent是基类,
package net.dp.composite.menu;
public abstract class MenuComponent {
public void add(MenuComponent menuComponent) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public void remove(MenuComponent menuComponent) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public MenuComponent getChild(int i) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public String getName() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public String getDescription() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public double getPrice() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public boolean isVegetarian() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public void print() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
}
Menu是枝干节点,
package net.dp.composite.menu;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Menu extends MenuComponent {
ArrayList<MenuComponent> menuComponents = new ArrayList<MenuComponent>();
String name;
String description;
public Menu(String name, String description) {
this.name = name;
this.description = description;
}
public void add(MenuComponent menuComponent) {
menuComponents.add(menuComponent);
}
public void remove(MenuComponent menuComponent) {
menuComponents.remove(menuComponent);
}
public MenuComponent getChild(int i) {
return (MenuComponent) menuComponents.get(i);
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public String getDescription() {
return description;
}
public void print() {
System.out.print("\n" + getName());
System.out.println(", " + getDescription());
System.out.println("---------------------");
Iterator<MenuComponent> iterator = menuComponents.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
MenuComponent menuComponent = iterator.next();
menuComponent.print();
}
}
}
MenuItem是叶子节点,
package net.dp.composite.menu;
public class MenuItem extends MenuComponent {
String name;
String description;
boolean vegetarian;
double price;
public MenuItem(String name, String description, boolean vegetarian,
double price) {
this.name = name;
this.description = description;
this.vegetarian = vegetarian;
this.price = price;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public String getDescription() {
return description;
}
public double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public boolean isVegetarian() {
return vegetarian;
}
public void print() {
System.out.print(" " + getName());
if (isVegetarian()) {
System.out.print("(v)");
}
System.out.println(", " + getPrice());
System.out.println(" -- " + getDescription());
}
}
Waitress作为Client,不需要区分枝干和叶子节点,这个区别对它是透明的。
package net.dp.composite.menu;
public class Waitress {
MenuComponent allMenus;
public Waitress(MenuComponent allMenus) {
this.allMenus = allMenus;
}
public void printMenu() {
allMenus.print();
}
}
测试程序,
package net.dp.composite.menu;
public class MenuTestDrive {
public static void main(String args[]) {
MenuComponent pancakeHouseMenu = new Menu("PANCAKE HOUSE MENU", "Breakfast");
MenuComponent dinerMenu = new Menu("DINER MENU", "Lunch");
MenuComponent cafeMenu = new Menu("CAFE MENU", "Dinner");
MenuComponent dessertMenu = new Menu("DESSERT MENU", "Dessert of course!");
MenuComponent coffeeMenu = new Menu("COFFEE MENU", "Stuff to go with your afternoon coffee");
MenuComponent allMenus = new Menu("ALL MENUS", "All menus combined");
allMenus.add(pancakeHouseMenu);
allMenus.add(dinerMenu);
allMenus.add(cafeMenu);
pancakeHouseMenu.add(new MenuItem("K&B's Pancake Breakfast", "Pancakes with scrambled eggs, and toast", true, 2.99));
pancakeHouseMenu.add(new MenuItem("Regular Pancake Breakfast", "Pancakes with fried eggs, sausage", false, 2.99));
pancakeHouseMenu.add(new MenuItem("Blueberry Pancakes", "Pancakes made with fresh blueberries, and blueberry syrup", true, 3.49));
pancakeHouseMenu.add(new MenuItem("Waffles", "Waffles, with your choice of blueberries or strawberries", true, 3.59));
dinerMenu.add(new MenuItem("Vegetarian BLT", "(Fakin') Bacon with lettuce & tomato on whole wheat", true, 2.99));
dinerMenu.add(new MenuItem("BLT", "Bacon with lettuce & tomato on whole wheat", false, 2.99));
dinerMenu.add(new MenuItem("Soup of the day", "A bowl of the soup of the day, with a side of potato salad", false, 3.29));
dinerMenu.add(new MenuItem("Hotdog", "A hot dog, with saurkraut, relish, onions, topped with cheese", false, 3.05));
dinerMenu.add(new MenuItem("Steamed Veggies and Brown Rice", "Steamed vegetables over brown rice", true, 3.99));
dinerMenu.add(new MenuItem("Pasta", "Spaghetti with Marinara Sauce, and a slice of sourdough bread", true, 3.89));
dinerMenu.add(dessertMenu);
dessertMenu.add(new MenuItem("Apple Pie", "Apple pie with a flakey crust, topped with vanilla icecream", true, 1.59));
dessertMenu.add(new MenuItem("Cheesecake", "Creamy New York cheesecake, with a chocolate graham crust", true, 1.99));
dessertMenu.add(new MenuItem("Sorbet", "A scoop of raspberry and a scoop of lime", true, 1.89));
cafeMenu.add(new MenuItem("Veggie Burger and Air Fries", "Veggie burger on a whole wheat bun, lettuce, tomato, and fries", true, 3.99));
cafeMenu.add(new MenuItem("Soup of the day", "A cup of the soup of the day, with a side salad", false, 3.69));
cafeMenu.add(new MenuItem("Burrito", "A large burrito, with whole pinto beans, salsa, guacamole", true, 4.29));
cafeMenu.add(coffeeMenu);
coffeeMenu.add(new MenuItem("Coffee Cake", "Crumbly cake topped with cinnamon and walnuts", true, 1.59));
coffeeMenu.add(new MenuItem("Bagel", "Flavors include sesame, poppyseed, cinnamon raisin, pumpkin", false, 0.69));
coffeeMenu.add(new MenuItem("Biscotti", "Three almond or hazelnut biscotti cookies", true, 0.89));
Waitress waitress = new Waitress(allMenus);
waitress.printMenu();
}
}
组合模式违反了“单一责任”的设计原则。组合模式不但要管理层次结构,还要执行菜单的操作。组合模式是以单一责任设计原则换取透明性。通过让组件的接口同时包含一些管理子节点和叶节点的操作,客户就可以将组合和叶节点一视同仁。也就是说,一个元素究竟是组合还是叶节点,对客户是透明的。
为基类MenuComponent增加一个createIterator()方法,实现组合迭代器。
package net.dp.composite.menuiterator;
import java.util.Iterator;
public abstract class MenuComponent {
public void add(MenuComponent menuComponent) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public void remove(MenuComponent menuComponent) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public MenuComponent getChild(int i) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public String getName() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public String getDescription() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public double getPrice() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public boolean isVegetarian() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public abstract Iterator<MenuComponent> createIterator();
public void print() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
}
对于叶子节点MenuItem,它不需要迭代出更多的节点,此时使用一个空迭代器NullIterator作为对象返回。
package net.dp.composite.menuiterator;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class NullIterator implements Iterator<MenuComponent> {
public MenuComponent next() {
return null;
}
public boolean hasNext() {
return false;
}
public void remove() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
}
package net.dp.composite.menuiterator;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class MenuItem extends MenuComponent {
String name;
String description;
boolean vegetarian;
double price;
public MenuItem(String name, String description, boolean vegetarian,
double price) {
this.name = name;
this.description = description;
this.vegetarian = vegetarian;
this.price = price;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public String getDescription() {
return description;
}
public double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public boolean isVegetarian() {
return vegetarian;
}
public Iterator<MenuComponent> createIterator() {
return new NullIterator();
}
public void print() {
System.out.print(" " + getName());
if (isVegetarian()) {
System.out.print("(v)");
}
System.out.println(", " + getPrice());
System.out.println(" -- " + getDescription());
}
}
作为枝干节点Menu,返回一个组合迭代器对象CompositeIterator,它的内部数据结构使用一个堆栈,利用它深度遍历树的所有节点。
package net.dp.composite.menuiterator;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Stack;
public class CompositeIterator implements Iterator<MenuComponent> {
Stack<Iterator<MenuComponent>> stack = new Stack<Iterator<MenuComponent>>();
public CompositeIterator(Iterator<MenuComponent> iterator) {
stack.push(iterator);
}
public MenuComponent next() {
if (hasNext()) {
Iterator<MenuComponent> iterator = stack.peek();
MenuComponent component = iterator.next();
if (component instanceof Menu) {
stack.push(component.createIterator());
}
return component;
} else {
return null;
}
}
public boolean hasNext() {
if (stack.empty()) {
return false;
} else {
Iterator<MenuComponent> iterator = stack.peek();
if (!iterator.hasNext()) {
stack.pop();
return hasNext();//递归调用,跳过所有叶子
} else {
return true;
}
}
}
public void remove() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
}
package net.dp.composite.menuiterator;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Menu extends MenuComponent {
ArrayList<MenuComponent> menuComponents = new ArrayList<MenuComponent>();
String name;
String description;
public Menu(String name, String description) {
this.name = name;
this.description = description;
}
public void add(MenuComponent menuComponent) {
menuComponents.add(menuComponent);
}
public void remove(MenuComponent menuComponent) {
menuComponents.remove(menuComponent);
}
public MenuComponent getChild(int i) {
return (MenuComponent)menuComponents.get(i);
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public String getDescription() {
return description;
}
public Iterator<MenuComponent> createIterator() {
return new CompositeIterator(menuComponents.iterator());
}
public void print() {
System.out.print("\n" + getName());
System.out.println(", " + getDescription());
System.out.println("---------------------");
Iterator<MenuComponent> iterator = menuComponents.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
MenuComponent menuComponent =
iterator.next();
menuComponent.print();
}
}
}
利用组合迭代器,Waitress可以遍历所有的节点,当前它会打印所有符合Vegetarian要求的节点。
package net.dp.composite.menuiterator;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class Waitress {
MenuComponent allMenus;
public Waitress(MenuComponent allMenus) {
this.allMenus = allMenus;
}
public void printMenu() {
allMenus.print();
}
public void printVegetarianMenu() {
Iterator<MenuComponent> iterator = allMenus.createIterator();
System.out.println("\nVEGETARIAN MENU\n----");
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
MenuComponent menuComponent = iterator.next();
try {
if (menuComponent.isVegetarian()) {
menuComponent.print();
}
} catch (UnsupportedOperationException e) {
}
}
}
}
测试程序,
package net.dp.composite.menuiterator;
public class MenuTestDrive {
public static void main(String args[]) {
MenuComponent pancakeHouseMenu =
new Menu("PANCAKE HOUSE MENU", "Breakfast");
MenuComponent dinerMenu =
new Menu("DINER MENU", "Lunch");
MenuComponent cafeMenu =
new Menu("CAFE MENU", "Dinner");
MenuComponent dessertMenu =
new Menu("DESSERT MENU", "Dessert of course!");
MenuComponent allMenus = new Menu("ALL MENUS", "All menus combined");
allMenus.add(pancakeHouseMenu);
allMenus.add(dinerMenu);
allMenus.add(cafeMenu);
pancakeHouseMenu.add(new MenuItem(
"K&B's Pancake Breakfast",
"Pancakes with scrambled eggs, and toast",
true,
2.99));
pancakeHouseMenu.add(new MenuItem(
"Regular Pancake Breakfast",
"Pancakes with fried eggs, sausage",
false,
2.99));
pancakeHouseMenu.add(new MenuItem(
"Blueberry Pancakes",
"Pancakes made with fresh blueberries, and blueberry syrup",
true,
3.49));
pancakeHouseMenu.add(new MenuItem(
"Waffles",
"Waffles, with your choice of blueberries or strawberries",
true,
3.59));
dinerMenu.add(new MenuItem(
"Vegetarian BLT",
"(Fakin') Bacon with lettuce & tomato on whole wheat",
true,
2.99));
dinerMenu.add(new MenuItem(
"BLT",
"Bacon with lettuce & tomato on whole wheat",
false,
2.99));
dinerMenu.add(new MenuItem(
"Soup of the day",
"A bowl of the soup of the day, with a side of potato salad",
false,
3.29));
dinerMenu.add(new MenuItem(
"Hotdog",
"A hot dog, with saurkraut, relish, onions, topped with cheese",
false,
3.05));
dinerMenu.add(new MenuItem(
"Steamed Veggies and Brown Rice",
"A medly of steamed vegetables over brown rice",
true,
3.99));
dinerMenu.add(new MenuItem(
"Pasta",
"Spaghetti with Marinara Sauce, and a slice of sourdough bread",
true,
3.89));
dinerMenu.add(dessertMenu);
dessertMenu.add(new MenuItem(
"Apple Pie",
"Apple pie with a flakey crust, topped with vanilla icecream",
true,
1.59));
dessertMenu.add(new MenuItem(
"Cheesecake",
"Creamy New York cheesecake, with a chocolate graham crust",
true,
1.99));
dessertMenu.add(new MenuItem(
"Sorbet",
"A scoop of raspberry and a scoop of lime",
true,
1.89));
cafeMenu.add(new MenuItem(
"Veggie Burger and Air Fries",
"Veggie burger on a whole wheat bun, lettuce, tomato, and fries",
true,
3.99));
cafeMenu.add(new MenuItem(
"Soup of the day",
"A cup of the soup of the day, with a side salad",
false,
3.69));
cafeMenu.add(new MenuItem(
"Burrito",
"A large burrito, with whole pinto beans, salsa, guacamole",
true,
4.29));
Waitress waitress = new Waitress(allMenus);
waitress.printVegetarianMenu();
}
}
10 状态模式-事物的状态
状态模式-允许对象在内部状态改变时改变它的行为,对象看起来修改了它的类。这个模式将状态封装成为独立的类,并将动作委托到代表当前状态的对象。使用组合通过简单引用不同的状态对象来造成类改变状态的假象。
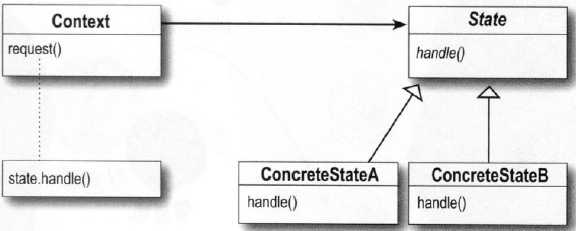
策略模式与状态模式-一般来说,我们把策略模式想成是除了继承之外的一种弹性替代方案。如果你使用继承定义了一个类的行为,你将被这个行为困住,甚至要修改它都很难。有了策略模式,你可以通过组合不同的对象来改变行为。我们把状态模式想成是不用在context中放置许多条件判断的替代方案。通过将行为包装进状态对象中,你可以通过在context内简单地改变状态对象来改变context的行为。
糖果机例子,它的状态图如下,
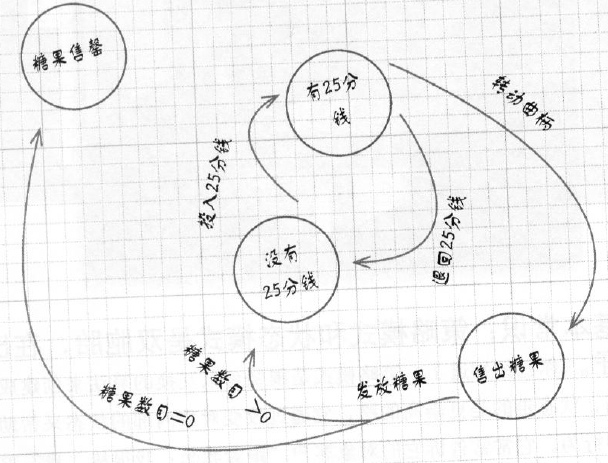
从图中我们可以分析出系统存在四种状态:没有25分钱(NO_QUARTER),有25分钱(HAS_QUARTER),糖果售罄(SOLD_OUT),出售糖果(SOLD)。将系统中可以发成的动作归纳为:投入25分钱(insertQuarter),退回25分钱(ejectQuarter),转动曲柄(turnCrank),发放糖果(dispense)。每种动作的发生,都会导致系统中状态的转换。
不使用状态模式,
package net.dp.state.gumball;
public class GumballMachine {
final static int SOLD_OUT = 0;
final static int NO_QUARTER = 1;
final static int HAS_QUARTER = 2;
final static int SOLD = 3;
int state = SOLD_OUT;
int count = 0;
public GumballMachine(int count) {
this.count = count;
if (count > 0) {
state = NO_QUARTER;
}
}
public void insertQuarter() {
if (state == HAS_QUARTER) {
System.out.println("You can't insert another quarter");
} else if (state == NO_QUARTER) {
state = HAS_QUARTER;
System.out.println("You inserted a quarter");
} else if (state == SOLD_OUT) {
System.out.println("You can't insert a quarter, the machine is sold out");
} else if (state == SOLD) {
System.out.println("Please wait, we're already giving you a gumball");
}
}
public void ejectQuarter() {
if (state == HAS_QUARTER) {
System.out.println("Quarter returned");
state = NO_QUARTER;
} else if (state == NO_QUARTER) {
System.out.println("You haven't inserted a quarter");
} else if (state == SOLD) {
System.out.println("Sorry, you already turned the crank");
} else if (state == SOLD_OUT) {
System.out.println("You can't eject, you haven't inserted a quarter yet");
}
}
public void turnCrank() {
if (state == SOLD) {
System.out.println("Turning twice doesn't get you another gumball!");
} else if (state == NO_QUARTER) {
System.out.println("You turned but there's no quarter");
} else if (state == SOLD_OUT) {
System.out.println("You turned, but there are no gumballs");
} else if (state == HAS_QUARTER) {
System.out.println("You turned...");
state = SOLD;
dispense();
}
}
public void dispense() {
if (state == SOLD) {
System.out.println("A gumball comes rolling out the slot");
count = count - 1;
if (count == 0) {
System.out.println("Oops, out of gumballs!");
state = SOLD_OUT;
} else {
state = NO_QUARTER;
}
} else if (state == NO_QUARTER) {
System.out.println("You need to pay first");
} else if (state == SOLD_OUT) {
System.out.println("No gumball dispensed");
} else if (state == HAS_QUARTER) {
System.out.println("No gumball dispensed");
}
}
public void refill(int numGumBalls) {
this.count = numGumBalls;
state = NO_QUARTER;
}
public String toString() {
StringBuffer result = new StringBuffer();
result.append("\nMighty Gumball, Inc.");
result.append("\nJava-enabled Standing Gumball Model #2004\n");
result.append("Inventory: " + count + " gumball");
if (count != 1) {
result.append("s");
}
result.append("\nMachine is ");
if (state == SOLD_OUT) {
result.append("sold out");
} else if (state == NO_QUARTER) {
result.append("waiting for quarter");
} else if (state == HAS_QUARTER) {
result.append("waiting for turn of crank");
} else if (state == SOLD) {
result.append("delivering a gumball");
}
result.append("\n");
return result.toString();
}
}
测试程序,
package net.dp.state.gumball;
public class GumballMachineTestDrive {
public static void main(String[] args) {
GumballMachine gumballMachine = new GumballMachine(5);
System.out.println(gumballMachine);
gumballMachine.insertQuarter();
gumballMachine.turnCrank();
System.out.println(gumballMachine);
gumballMachine.insertQuarter();
gumballMachine.ejectQuarter();
gumballMachine.turnCrank();
System.out.println(gumballMachine);
gumballMachine.insertQuarter();
gumballMachine.turnCrank();
gumballMachine.insertQuarter();
gumballMachine.turnCrank();
gumballMachine.ejectQuarter();
System.out.println(gumballMachine);
gumballMachine.insertQuarter();
gumballMachine.insertQuarter();
gumballMachine.turnCrank();
gumballMachine.insertQuarter();
gumballMachine.turnCrank();
gumballMachine.insertQuarter();
gumballMachine.turnCrank();
System.out.println(gumballMachine);
}
}
现在我们使用状态模式,将四种状态抽象成类,
状态接口,
package net.dp.state.gumballstate;
public interface State {
public void insertQuarter();
public void ejectQuarter();
public void turnCrank();
public void dispense();
}
四种状态,我们可以发现,所有的动作实现其实就是当前状态至其他几种状态的转变过程。这一过程很好的融入在各个状态子类中。
package net.dp.state.gumballstate;
public class HasQuarterState implements State {
GumballMachine gumballMachine;
public HasQuarterState(GumballMachine gumballMachine) {
this.gumballMachine = gumballMachine;
}
public void insertQuarter() {
System.out.println("You can't insert another quarter");
}
public void ejectQuarter() {
System.out.println("Quarter returned");
gumballMachine.setState(gumballMachine.getNoQuarterState());
}
public void turnCrank() {
System.out.println("You turned...");
gumballMachine.setState(gumballMachine.getSoldState());
}
public void dispense() {
System.out.println("No gumball dispensed");
}
public String toString() {
return "waiting for turn of crank";
}
}
package net.dp.state.gumballstate;
public class NoQuarterState implements State {
GumballMachine gumballMachine;
public NoQuarterState(GumballMachine gumballMachine) {
this.gumballMachine = gumballMachine;
}
public void insertQuarter() {
System.out.println("You inserted a quarter");
gumballMachine.setState(gumballMachine.getHasQuarterState());
}
public void ejectQuarter() {
System.out.println("You haven't inserted a quarter");
}
public void turnCrank() {
System.out.println("You turned, but there's no quarter");
}
public void dispense() {
System.out.println("You need to pay first");
}
public String toString() {
return "waiting for quarter";
}
}
package net.dp.state.gumballstate;
public class SoldOutState implements State {
GumballMachine gumballMachine;
public SoldOutState(GumballMachine gumballMachine) {
this.gumballMachine = gumballMachine;
}
public void insertQuarter() {
System.out
.println("You can't insert a quarter, the machine is sold out");
}
public void ejectQuarter() {
System.out
.println("You can't eject, you haven't inserted a quarter yet");
}
public void turnCrank() {
System.out.println("You turned, but there are no gumballs");
}
public void dispense() {
System.out.println("No gumball dispensed");
}
public String toString() {
return "sold out";
}
}
package net.dp.state.gumballstate;
public class SoldState implements State {
GumballMachine gumballMachine;
public SoldState(GumballMachine gumballMachine) {
this.gumballMachine = gumballMachine;
}
public void insertQuarter() {
System.out.println("Please wait, we're already giving you a gumball");
}
public void ejectQuarter() {
System.out.println("Sorry, you already turned the crank");
}
public void turnCrank() {
System.out.println("Turning twice doesn't get you another gumball!");
}
public void dispense() {
gumballMachine.releaseBall();
if (gumballMachine.getCount() > 0) {
gumballMachine.setState(gumballMachine.getNoQuarterState());
} else {
System.out.println("Oops, out of gumballs!");
gumballMachine.setState(gumballMachine.getSoldOutState());
}
}
public String toString() {
return "dispensing a gumball";
}
}
糖果机中没有了各种状态互相之间转换的繁杂逻辑,
package net.dp.state.gumballstate;
public class GumballMachine {
State soldOutState;
State noQuarterState;
State hasQuarterState;
State soldState;
State state = soldOutState;
int count = 0;
public GumballMachine(int numberGumballs) {
soldOutState = new SoldOutState(this);
noQuarterState = new NoQuarterState(this);
hasQuarterState = new HasQuarterState(this);
soldState = new SoldState(this);
this.count = numberGumballs;
if (numberGumballs > 0) {
state = noQuarterState;
}
}
public void insertQuarter() {
state.insertQuarter();
}
public void ejectQuarter() {
state.ejectQuarter();
}
public void turnCrank() {
state.turnCrank();
state.dispense();
}
void setState(State state) {
this.state = state;
}
void releaseBall() {
System.out.println("A gumball comes rolling out the slot...");
if (count != 0) {
count = count - 1;
}
}
int getCount() {
return count;
}
void refill(int count) {
this.count = count;
state = noQuarterState;
}
public State getState() {
return state;
}
public State getSoldOutState() {
return soldOutState;
}
public State getNoQuarterState() {
return noQuarterState;
}
public State getHasQuarterState() {
return hasQuarterState;
}
public State getSoldState() {
return soldState;
}
public String toString() {
StringBuffer result = new StringBuffer();
result.append("\nMighty Gumball, Inc.");
result.append("\nJava-enabled Standing Gumball Model #2004");
result.append("\nInventory: " + count + " gumball");
if (count != 1) {
result.append("s");
}
result.append("\n");
result.append("Machine is " + state + "\n");
return result.toString();
}
}
测试程序,
package net.dp.state.gumballstate;
public class GumballMachineTestDrive {
public static void main(String[] args) {
GumballMachine gumballMachine = new GumballMachine(5);
System.out.println(gumballMachine);
gumballMachine.insertQuarter();
gumballMachine.turnCrank();
System.out.println(gumballMachine);
gumballMachine.insertQuarter();
gumballMachine.turnCrank();
gumballMachine.insertQuarter();
gumballMachine.turnCrank();
System.out.println(gumballMachine);
}
}
使用状态模式,对于系统新增状态也会变得非常简单,现在增加一种情况,“当曲柄被转动时,有10%机率掉下来的是两颗糖果”
package net.dp.state.gumballstatewinner;
public class WinnerState implements State {
GumballMachine gumballMachine;
public WinnerState(GumballMachine gumballMachine) {
this.gumballMachine = gumballMachine;
}
public void insertQuarter() {
System.out.println("Please wait, we're already giving you a Gumball");
}
public void ejectQuarter() {
System.out.println("Please wait, we're already giving you a Gumball");
}
public void turnCrank() {
System.out.println("Turning again doesn't get you another gumball!");
}
public void dispense() {
System.out.println("YOU'RE A WINNER! You get two gumballs for your quarter");
gumballMachine.releaseBall();
if (gumballMachine.getCount() == 0) {
gumballMachine.setState(gumballMachine.getSoldOutState());
} else {
gumballMachine.releaseBall();
if (gumballMachine.getCount() > 0) {
gumballMachine.setState(gumballMachine.getNoQuarterState());
} else {
System.out.println("Oops, out of gumballs!");
gumballMachine.setState(gumballMachine.getSoldOutState());
}
}
}
public String toString() {
return "despensing two gumballs for your quarter, because YOU'RE A WINNER!";
}
}
修改有25分钱状态,增加其触发至“10%机率获得两颗糖果”的状态
package net.dp.state.gumballstatewinner;
import java.util.Random;
public class HasQuarterState implements State {
Random randomWinner = new Random(System.currentTimeMillis());
GumballMachine gumballMachine;
public HasQuarterState(GumballMachine gumballMachine) {
this.gumballMachine = gumballMachine;
}
public void insertQuarter() {
System.out.println("You can't insert another quarter");
}
public void ejectQuarter() {
System.out.println("Quarter returned");
gumballMachine.setState(gumballMachine.getNoQuarterState());
}
public void turnCrank() {
System.out.println("You turned...");
int winner = randomWinner.nextInt(10);
if ((winner == 0) && (gumballMachine.getCount() > 1)) {
gumballMachine.setState(gumballMachine.getWinnerState());
} else {
gumballMachine.setState(gumballMachine.getSoldState());
}
}
public void dispense() {
System.out.println("No gumball dispensed");
}
public String toString() {
return "waiting for turn of crank";
}
}
糖果机中新增一种状态
package net.dp.state.gumballstatewinner;
public class GumballMachine {
State soldOutState;
State noQuarterState;
State hasQuarterState;
State soldState;
State winnerState;
State state = soldOutState;
int count = 0;
public GumballMachine(int numberGumballs) {
soldOutState = new SoldOutState(this);
noQuarterState = new NoQuarterState(this);
hasQuarterState = new HasQuarterState(this);
soldState = new SoldState(this);
winnerState = new WinnerState(this);
this.count = numberGumballs;
if (numberGumballs > 0) {
state = noQuarterState;
}
}
public void insertQuarter() {
state.insertQuarter();
}
public void ejectQuarter() {
state.ejectQuarter();
}
public void turnCrank() {
state.turnCrank();
state.dispense();
}
void setState(State state) {
this.state = state;
}
void releaseBall() {
System.out.println("A gumball comes rolling out the slot...");
if (count != 0) {
count = count - 1;
}
}
int getCount() {
return count;
}
void refill(int count) {
this.count = count;
state = noQuarterState;
}
public State getState() {
return state;
}
public State getSoldOutState() {
return soldOutState;
}
public State getNoQuarterState() {
return noQuarterState;
}
public State getHasQuarterState() {
return hasQuarterState;
}
public State getSoldState() {
return soldState;
}
public State getWinnerState() {
return winnerState;
}
public String toString() {
StringBuffer result = new StringBuffer();
result.append("\nMighty Gumball, Inc.");
result.append("\nJava-enabled Standing Gumball Model #2004");
result.append("\nInventory: " + count + " gumball");
if (count != 1) {
result.append("s");
}
result.append("\n");
result.append("Machine is " + state + "\n");
return result.toString();
}
}
测试程序,
package net.dp.state.gumballstatewinner;
public class GumballMachineTestDrive {
public static void main(String[] args) {
GumballMachine gumballMachine =
new GumballMachine(10);
System.out.println(gumballMachine);
gumballMachine.insertQuarter();
gumballMachine.turnCrank();
gumballMachine.insertQuarter();
gumballMachine.turnCrank();
System.out.println(gumballMachine);
gumballMachine.insertQuarter();
gumballMachine.turnCrank();
gumballMachine.insertQuarter();
gumballMachine.turnCrank();
System.out.println(gumballMachine);
gumballMachine.insertQuarter();
gumballMachine.turnCrank();
gumballMachine.insertQuarter();
gumballMachine.turnCrank();
System.out.println(gumballMachine);
gumballMachine.insertQuarter();
gumballMachine.turnCrank();
gumballMachine.insertQuarter();
gumballMachine.turnCrank();
System.out.println(gumballMachine);
gumballMachine.insertQuarter();
gumballMachine.turnCrank();
gumballMachine.insertQuarter();
gumballMachine.turnCrank();
System.out.println(gumballMachine);
}
}
11.代理模式-控制对象访问
代理模式-为另一个对象提供一个替身或占位符以控制对这个对象的访问。使用代理模式创建代表对象,让代表对象控制某对象的访问,被代理的对象可以是远程的对象、创建开销大的对象或需要安全控制的对象。
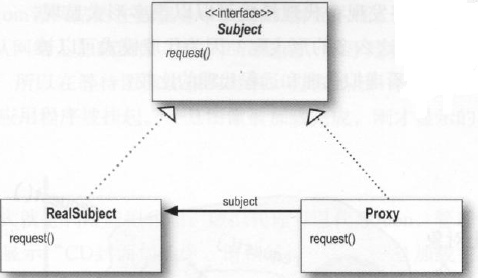
下面演示一种创建开销大的对象的代理的用法,ImageProxy首先创建一个ImageIcon,然后开始从网络URL上加载图片。在加载过程中,ImageProxy显示“CD封面加载中,请稍候……”。当图片加载完毕,ImageProxy把所有方法调用委托给真正的ImageIcon,这些方法包括了paintIcon(),getWidth()和getHeight()。如果用户请求新的图像,我们就创建新的代理,重复这样的过程。
Image组件,
package net.dp.proxy.virtualproxy;
import java.awt.Graphics;
import javax.swing.Icon;
import javax.swing.JComponent;
class ImageComponent extends JComponent {
/**
*
*/
private static final long serialVersionUID = -4028999850832876573L;
private Icon icon;
public ImageComponent(Icon icon) {
this.icon = icon;
}
public void setIcon(Icon icon) {
this.icon = icon;
}
public void paintComponent(Graphics g) {
super.paintComponent(g);
int w = icon.getIconWidth();
int h = icon.getIconHeight();
int x = (800 - w)/2;
int y = (600 - h)/2;
icon.paintIcon(this, g, x, y);
}
}
其中对于ImageIcon,使用了代理,
package net.dp.proxy.virtualproxy;
import java.awt.Component;
import java.awt.Graphics;
import java.net.URL;
import javax.swing.Icon;
import javax.swing.ImageIcon;
class ImageProxy implements Icon {
ImageIcon imageIcon;
URL imageURL;
Thread retrievalThread;
boolean retrieving = false;
public ImageProxy(URL url) { imageURL = url; }
public int getIconWidth() {
if (imageIcon != null) {
return imageIcon.getIconWidth();
} else {
return 800;
}
}
public int getIconHeight() {
if (imageIcon != null) {
return imageIcon.getIconHeight();
} else {
return 600;
}
}
public void paintIcon(final Component c, Graphics g, int x, int y) {
if (imageIcon != null) {
imageIcon.paintIcon(c, g, x, y);
} else {
g.drawString("Loading CD cover, please wait...", x+300, y+190);
if (!retrieving) {
retrieving = true;
retrievalThread = new Thread(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
try {
imageIcon = new ImageIcon(imageURL, "CD Cover");
c.repaint();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
retrievalThread.start();
}
}
}
}
最终在Image组件中组装Icon时,创建了Icon的代理对象,
package net.dp.proxy.virtualproxy;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import java.net.MalformedURLException;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import java.util.Hashtable;
import javax.swing.Icon;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JMenu;
import javax.swing.JMenuBar;
import javax.swing.JMenuItem;
public class ImageProxyTestDrive {
ImageComponent imageComponent;
JFrame frame = new JFrame("CD Cover Viewer");
JMenuBar menuBar;
JMenu menu;
Hashtable<String, String> cds = new Hashtable<String, String>();
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
@SuppressWarnings("unused")
ImageProxyTestDrive testDrive = new ImageProxyTestDrive();
}
public ImageProxyTestDrive() throws Exception {
cds.put("Ambient: Music for Airports",
"http://images.amazon.com/images/P/B000003S2K.01.LZZZZZZZ.jpg");
cds.put("Buddha Bar",
"http://images.amazon.com/images/P/B00009XBYK.01.LZZZZZZZ.jpg");
cds.put("Ima",
"http://images.amazon.com/images/P/B000005IRM.01.LZZZZZZZ.jpg");
cds.put("Karma",
"http://images.amazon.com/images/P/B000005DCB.01.LZZZZZZZ.gif");
cds.put("MCMXC A.D.",
"http://images.amazon.com/images/P/B000002URV.01.LZZZZZZZ.jpg");
cds.put("Northern Exposure",
"http://images.amazon.com/images/P/B000003SFN.01.LZZZZZZZ.jpg");
cds.put("Selected Ambient Works, Vol. 2",
"http://images.amazon.com/images/P/B000002MNZ.01.LZZZZZZZ.jpg");
URL initialURL = new URL((String) cds
.get("Selected Ambient Works, Vol. 2"));
menuBar = new JMenuBar();
menu = new JMenu("Favorite CDs");
menuBar.add(menu);
frame.setJMenuBar(menuBar);
for (Enumeration<String> e = cds.keys(); e.hasMoreElements();) {
String name = (String) e.nextElement();
JMenuItem menuItem = new JMenuItem(name);
menu.add(menuItem);
menuItem.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event) {
imageComponent.setIcon(new ImageProxy(getCDUrl(event
.getActionCommand())));
frame.repaint();
}
});
}
// set up frame and menus
Icon icon = new ImageProxy(initialURL);
imageComponent = new ImageComponent(icon);
frame.getContentPane().add(imageComponent);
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setSize(800, 600);
frame.setVisible(true);
}
URL getCDUrl(String name) {
try {
return new URL((String) cds.get(name));
} catch (MalformedURLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
}